Table of Contents:
When it comes to choosing the ideal backup power for your home, home battery backup systems and traditional generators are two of the most popular options, providing a reliable power source during outages. Many people are curious about which option is better and how to choose the most suitable one for their needs.
In this article, we will address these questions, provide explanations about these two options, discuss their pros and cons, and guide you in selecting the best fit according to your requirements.
Home Battery Backup Systems

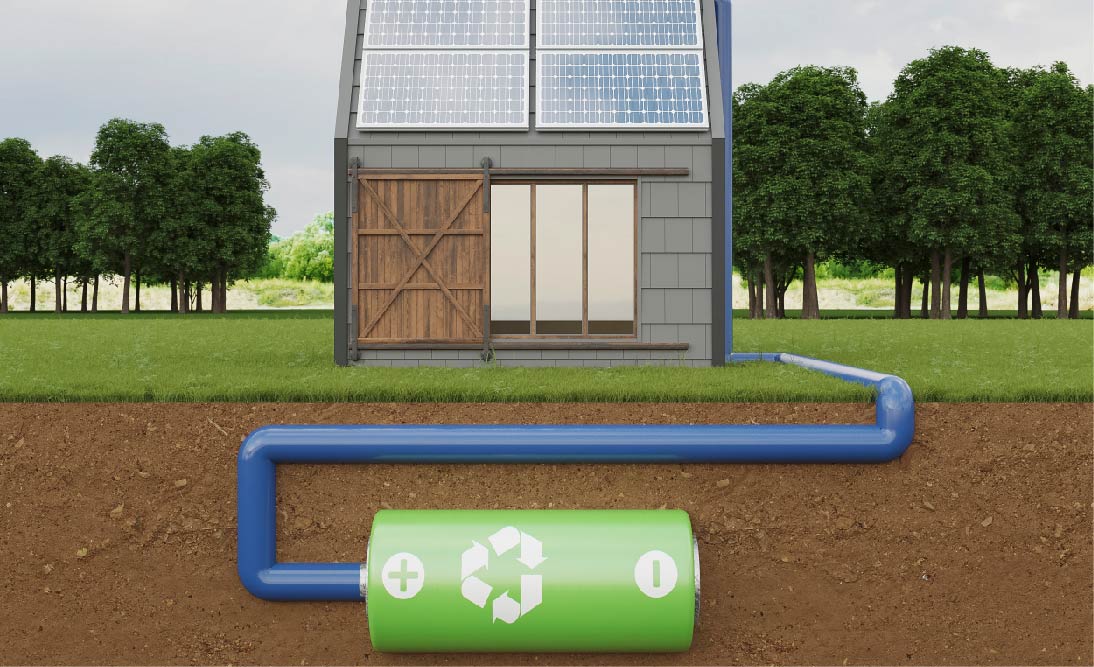
Home battery backup systems are devices designed to store electrical energy for later use, serving as a backup power source or an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) during outages or when electricity demand exceeds supply.
They offer a clean and efficient way to store and use electricity, providing peace of mind during power outages and helping homeowners manage their energy consumption and costs. There are different types of home battery backup systems. A solar generator is one of the popular options.
Main Components of Home Battery Backup Systems:
-
Battery Storage Unit: At the heart of the system, this component stores electrical energy in the form of direct current (DC). Common battery types used are lithium-ion and LiFePO4 (LFP). These batteries come in various capacities, which determine the amount of energy that can be stored.
-
Inverter: An inverter converts the DC power stored in the battery into alternating current (AC), which is the standard type of electricity used in most homes. This AC power is then distributed to your household appliances and devices.
-
Charge Controller: The charge controller manages the flow of electricity from the solar panels or grid to the battery. It ensures that the battery is charged efficiently and prevents overcharging or over-discharging, which can damage the battery.
-
Solar Panels (Optional): Some home battery backup systems can be charged by solar panels. If your system includes solar panels, they capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity, which is then directed to the battery through the charge controller.
How Do They Work?
1. Charging: The battery backup system can be charged in two ways:
-
Solar Charging (if equipped): Solar panels capture sunlight and generate DC electricity. This electricity is directed to the battery via the charge controller.
-
Grid Charging: When the grid is operational, the system can be charged by drawing electricity from the grid. This charging mode typically occurs during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower.
2. Energy Storage: The DC electricity generated or received is stored in the battery for later use. The battery's capacity determines how much energy can be stored.
3. Inverter Conversion: When you need power, the inverter converts the stored DC electricity into AC power, which is compatible with your household appliances and devices.
4. Power Distribution: The AC power is distributed to your home's electrical panel, allowing you to use it as needed. The distribution typically includes power outlets and circuits connected to essential appliances and devices.
5. Power during Outages: During a power outage, the battery backup system automatically switches to provide power, ensuring that your critical appliances and devices continue to function. This seamless transition helps maintain essential services and convenience during outages.
6. Recharging: Once power is restored to the grid, the system can recharge the battery using grid electricity or, if equipped, solar power. This ensures that the battery is ready for the next outage or high-demand period.
Traditional Home Generators

Traditional home generators, often known as standby generators or backup generators, are devices that provide a secondary source of electrical power during outages or when the primary power supply is unavailable. These generators typically run on fossil fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, or natural gas.
Traditional home generators offer a reliable source of backup power during outages and are suitable for providing electricity to your entire home. However, they require a steady supply of fuel and regular maintenance to remain operational. Standby generators are often used in homes and businesses to ensure continuous power, especially in areas prone to frequent outages.
Main Components of Traditional Home Generators:
-
Engine: The engine is the core component of a traditional generator. It can be powered by gasoline, diesel, propane, or natural gas. The engine's role is to generate mechanical energy that drives the generator's alternator or generator head.
-
Alternator (Generator Head): The alternator, also known as the generator head, converts the mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. It produces alternating current (AC), the standard form of electricity used in homes.
-
Fuel System: Traditional generators require a steady supply of fuel to operate. This includes fuel tanks for gasoline or diesel generators and connections to natural gas or propane sources for gas-powered generators.
-
Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator controls the generator's output voltage to ensure it remains at the desired level, typically 120/240 volts for residential applications. It prevents voltage spikes or drops that could damage sensitive electronics.
-
Control Panel: The control panel typically includes various controls and indicators, such as an on/off switch, circuit breakers, voltage and frequency gauges, and warning lights. It allows users to monitor and control the generator's operation.
-
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): An ATS is a critical component for standby generators. It connects the generator to your home's electrical system and automatically switches power sources during an outage. When it detects a power interruption, it disconnects your home from the grid and connects it to the generator, ensuring a seamless transition.
How Do They Work?
-
Detection of Power Outage: When the traditional generator is installed with an ATS, it continuously monitors the incoming utility power. If it detects an interruption in the grid power, it initiates the startup sequence.
-
Engine Start: The engine is started automatically when a power outage is detected. If the generator is manually operated, the user starts the engine.
-
Mechanical Energy Generation: The engine produces mechanical energy, typically in the form of rotational motion.
-
Electrical Energy Generation: The alternator, connected to the engine, converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. It generates AC electricity.
-
Power Distribution: The AC electricity is then distributed to your home's electrical panel through the ATS, which automatically disconnects your home from the grid and connects it to the generator. This provides power to your home.
-
Continuous Operation: The generator continues to run as long as it has a fuel supply. The generator's control panel monitors voltage and frequency to ensure stable power output.
-
Restoration of Grid Power: When grid power is restored, the ATS detects this and switches the power source back to the grid, disconnecting the generator.
Pros and Cons Of Battery Home Generators and Traditional Generators

These two options can be used as home backup power solutions, each with its advantages and disadvantages. To gain a clear understanding of their pros and cons, please refer to the table below:
Battery Home Generators
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
Clean and renewable energy source |
Limited capacity for prolonged outages |
|
Quiet operation |
Dependence on sunlight or grid for charging |
|
Low maintenance |
Initial cost and battery replacement |
|
Easy installation and portability |
Limited power output compared to traditional generators |
|
Suitable for intermittent use |
May not support high-demand appliances |
|
Reduced carbon footprint |
Limited energy storage for long outages |
|
Can integrate with solar panels (optional) |
Limited capacity for high-wattage appliances |
Traditional Generators
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
High power output |
Reliance on fossil fuels and fuel storage |
|
Suitable for prolonged outages |
Noisy operation and emissions |
|
Can power high-wattage appliances |
Regular fuel maintenance and refueling |
|
Automatic transfer switches for seamless use |
Maintenance of internal combustion engine |
|
No dependence on sunlight or grid |
Higher emissions and environmental impact |
|
Reliable power source during extended outages |
Installation complexity and cost |
|
Can power the entire home |
Large size and fixed installation |
Understanding the pros and cons of these options will provide you with a fundamental foundation for selecting the ideal one, which we will discuss next.
How To Choose The Right One?

From above, you’ve already had a general idea about the pros and cons of battery Home generators and traditional Generators, and some of the main differences between them. Now, let’s talk about which one is better.
Here, it is important to know that better doesn’t mean cheaper. You first have to know your power needs and budget before purchasing one.
Power Needs
-
Battery Home Generators: If you have relatively modest power needs during outages and mainly want to keep essential devices running, a battery home generator might be sufficient. They are suitable for intermittent use and can power basic appliances and devices.
-
Traditional Generators: If you have high power demands, need to run large appliances, or have a whole-house power requirement, a traditional generator with higher wattage capacity is the better choice.
Budget
-
Battery Home Generators: While they have higher upfront costs, battery home generators often have lower operating costs and reduced maintenance needs. Consider your budget not just for the initial purchase but also for long-term usage.
-
Traditional Generators: Traditional generators may have a lower initial cost, but the ongoing expenses of fuel, maintenance, and potential repairs should be factored into your budget.
Fuel Availability
-
Battery Home Generators: These generators are not dependent on fuel, making them suitable for locations where fuel availability might be limited or during fuel shortages.
-
Traditional Generators: Traditional generators require a consistent supply of fuel, so it's essential to ensure a reliable source of gasoline, diesel, propane, or natural gas.
Environmental Impact
-
Battery Home Generators: If you prioritize environmental sustainability and want to reduce your carbon footprint, battery home generators, which rely on clean and renewable energy sources, are the eco-friendly choice.
-
Traditional Generators: Traditional generators emit greenhouse gases and have a higher environmental impact due to their reliance on fossil fuels.
Maintenance
-
Battery Home Generators: These generators typically require minimal maintenance. Battery replacement may be necessary after several years.
-
Traditional Generators: Traditional generators need regular maintenance, including fuel system checks and engine upkeep. This ongoing maintenance can be more involved and costly.
Portability and Installation
-
Battery Home Generators: They are often portable and easier to install, providing flexibility in placement. This makes them suitable for homeowners who may relocate or have limited space for a fixed installation.
-
Traditional Generators: Traditional generators are typically installed in a fixed location and may require more complex installation, such as connecting to natural gas lines or large fuel tanks.
Noise Levels
-
Battery Home Generators: Battery home generators operate quietly, offering a peaceful backup power solution.
-
Traditional Generators: Traditional generators can be noisy due to their internal combustion engines, which can be a consideration for noise-sensitive environments.
Runtime and Capacity
-
Battery Home Generators: Battery home generators have limited energy storage, making them suitable for shorter outages or as a complement to solar panels. Their runtime depends on the battery's capacity.
-
Traditional Generators: Traditional generators have longer runtime and can provide power during extended outages without concerns about battery depletion.
Choosing between the two depends on your specific needs and priorities. Battery home generators are ideal for clean energy and intermittent use, while traditional generators offer high power output and reliability during extended outages. Consider factors such as environmental concerns, power requirements, and budget when making your decision.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the choice between Home Battery Backup Systems and Traditional Generators for your backup power needs depends on various factors, and both options have their strengths and limitations.
Home Battery Backup Systems, with their clean and renewable energy sources, offer a quiet and environmentally friendly solution. They are ideal for modest power needs, intermittent use, and those looking to reduce their carbon footprint. These systems are low maintenance, easy to install, and can integrate with solar panels for additional sustainability.
On the other hand, Traditional Generators provide high power output and reliability during extended outages, making them suitable for homes with larger power demands. They operate independently of sunlight or the grid and can power the entire house. However, they come with noise and emissions, require regular maintenance, and rely on fuel availability.
To make the right choice, it's crucial to assess your power requirements, budget, environmental concerns, and other preferences. Understanding the pros and cons of each option is the first step toward selecting the ideal backup power solution that aligns with your specific needs and priorities. Your decision should be based on what works best for you, ensuring that your home remains powered and comfortable during outages.
Explore POWEREPUBLIC Solar Generator Kits as One of The Options For Home Battery Backup.