Table of Contents:
In today’s world, where sustainable living and energy independence are increasingly important, off-grid batteries have become essential for those living away from the electricity grid. This guide dives into the key challenges and considerations surrounding off-grid batteries, vital for anyone seeking a self-reliant and eco-friendly lifestyle. It comprehensively covers the different types of batteries, such as LiFePO4 and lithium-ion, their pros and cons, and critical factors like capacity, lifespan, efficiency, and cost.
The guide also compares traditional batteries with portable power stations, spotlighting models like POWEREPUBLIC’s T1200, T2200, and T3000, and addresses common queries about their lifespan, value, and appropriate sizing. This article is an essential resource for understanding and choosing the right off-grid battery solution, balancing efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness for an empowered greener life.
Off-Grid Batteries Overview
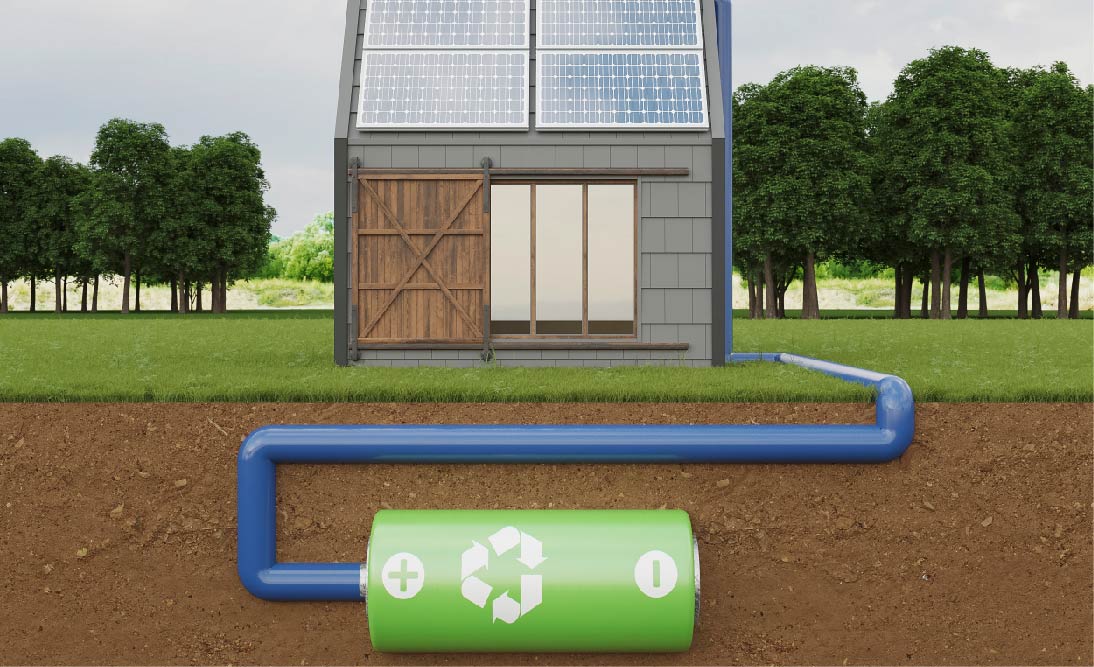
Off-grid batteries are essential components in off-grid energy systems, which are systems not connected to the main electricity grid. These batteries store electricity generated from renewable sources like solar panels or wind turbines, allowing for power usage even when the energy source isn't actively generating electricity (like at night or on cloudy days for solar panels). Here's a brief overview:
What are Off-Grid Batteries?
Off-grid batteries are specially designed to store electricity for use in remote or standalone power systems. They differ from grid-tied storage systems as they must be able to provide all the energy needs of a household or facility, often for several days.

How Do Off-Grid Batteries Work?
These batteries store electrical energy as chemical energy and release it as needed. During the day, for example, solar panels generate electricity. Excess electricity not immediately used is stored in these batteries. At night, or when the solar panels aren't generating electricity, the stored energy in the batteries is converted back into electrical energy.
Types of Off-Grid Batteries
-
Lead-Acid Batteries: Traditional, and more affordable, but require maintenance and have a shorter lifespan.
-
Lithium-ion batteries: More expensive upfront but offer longer lifespans, higher efficiencies, and require less maintenance. Many batteries these days use lithium-ion technology.
-
Saltwater Batteries: An emerging technology, known for being environmentally friendly but currently less efficient and more expensive.
Price of Off-Grid Batteries
-
The cost of off-grid batteries can vary widely depending on the type, capacity, and brand.
-
Lead-acid batteries may range from a few hundred to a couple of thousand dollars.
-
Lithium-ion batteries typically cost several thousand dollars but may be more cost-effective in the long run due to their longer lifespan and better efficiency.
-
Prices are subject to change based on technology advancements, market demand, and other economic factors.
Considerations for Choosing Off-Grid Batteries
-
Capacity & Power: Determining how much energy you need to store and the power required by your appliances.
-
Lifespan & Efficiency: Considering how long the batteries will last and their efficiency in storing and releasing energy.
-
Cost & Maintenance: Balancing the upfront cost with long-term maintenance requirements and replacement costs.
-
Environmental Impact: Some users might prefer environmentally friendly options, like saltwater batteries.
Off-grid batteries are a critical part of sustainable living and renewable energy systems, especially in remote areas without reliable access to the main power grid. Advances in battery technology continue to improve their efficiency, capacity, and affordability, making off-grid living more accessible and sustainable.
Off-Grid Batteries: LiFePO4 vs. Lithium-ion
We know that LiFePO4 and Lithium-ion batteries are used more frequently than other types of batteries. So knowing the difference between them will help you make better decisions. Both have unique characteristics that make them suitable for different needs and scenarios.
Here's an overview of both types:
Chemistry and Composition
-
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate): These batteries use lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. They are known for their thermal stability, long cycle life, and safety.
-
Lithium-ion: Traditional lithium-ion batteries typically use lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) or other lithium-metal oxides in the cathode. They are known for their high energy density and efficiency.
Safety and Thermal Stability
-
LiFePO4: These batteries are generally considered safer, as they are more stable and less prone to overheating or thermal runaway. This makes them a preferred choice in applications where safety is a major concern.
-
Lithium-ion: While they are generally safe, traditional lithium-ion batteries have a higher risk of overheating and can be more susceptible to thermal runaway, especially if improperly managed or damaged.
Energy Density and Efficiency
-
LiFePO4: These batteries have a lower energy density compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This means they are larger and heavier for the same storage capacity.
-
Lithium-ion: They have a higher energy density, providing more power for a given size and weight, which is beneficial in applications where space and weight are constraints.
Lifespan and Cycle Life
-
LiFePO4: These batteries often have a longer cycle life, sometimes exceeding 2000 cycles. This makes them more suitable for applications where the battery is regularly charged and discharged, like in off-grid systems.
-
Lithium-ion: They generally have a shorter cycle life compared to LiFePO4, which can be a consideration in systems where the battery is frequently cycled.
Cost
-
LiFePO4: Initially, these batteries tend to be more expensive than traditional lithium-ion batteries, but their longer lifespan can make them more cost-effective over time.
-
Lithium-ion: They are usually less expensive upfront but may incur higher costs over the long term due to a shorter lifespan and potential replacement needs.
Environmental Impact
-
LiFePO4: These batteries are often considered more environmentally friendly due to their more stable chemistry and the use of iron, which is less toxic than cobalt.
-
Lithium-ion: The use of cobalt and other metals in traditional lithium-ion batteries raises concerns about environmental impact and sustainable sourcing.
Application Suitability
-
LiFePO4: Due to their safety, longevity, and stability, LiFePO4 batteries are highly suitable for off-grid energy systems, particularly in residential or long-term deployment scenarios.
-
Lithium-ion: They are often preferred in applications where high energy density is crucial, such as in electric vehicles or portable electronics.

So, the choice between LiFePO4 and traditional lithium-ion batteries for off-grid systems depends on factors like the required energy density, safety considerations, budget constraints, and the expected frequency of charge-discharge cycles. LiFePO4 batteries are generally preferred for their safety and longevity, especially in stationary off-grid applications, while traditional lithium-ion batteries are favored in applications where size and weight are critical.
Pros and Cons of Off-Grid Batteries
Off-grid batteries, essential in storing energy for homes and systems not connected to the main electricity grid, have several pros and cons that are important to consider. Here's an overview:
Pros of Off-Grid Batteries
-
Energy Independence: They provide a reliable power source, enabling users to be independent of the utility grid. This is particularly beneficial in remote locations where grid access is not feasible or reliable.
-
Renewable Energy Utilization: Off-grid batteries allow for effective use of renewable energy sources like solar or wind by storing excess energy generated for use when the source isn't producing (e.g., solar energy at night).
-
Reduced Environmental Impact: When paired with renewable energy sources, these batteries can significantly reduce carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Emergency Power Supply: In the event of power outages or natural disasters, off-grid batteries can provide a crucial power supply, ensuring continued access to electricity.
-
Potential Savings: Over time, using off-grid batteries can lead to cost savings, particularly where grid electricity is expensive or where users can avoid the cost of connecting to a distant grid.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: Off-grid systems can be scaled to meet specific power needs and can be expanded as those needs grow.
Cons of Off-Grid Batteries
-
High Initial Investment: The upfront cost of off-grid battery systems (including batteries, inverters, and other components) can be quite high.
-
Maintenance and Replacement Costs: Some batteries require regular maintenance, and all batteries have a limited lifespan, necessitating eventual replacement.
-
Limited Energy Storage Capacity: The capacity of batteries to store energy can limit the electricity available, especially during prolonged periods of low renewable energy generation (like several cloudy days in a row for solar systems).
-
Space Requirements: Large battery banks can require significant space, which might be a constraint in some settings.
-
Complexity and Expertise Required: Designing, installing, and maintaining an off-grid system requires a certain level of expertise and can be more complex than simply connecting to the grid.
-
Environmental Concerns: While better for the environment than fossil fuels, the production, and disposal of batteries do have environmental impacts, especially concerning the mining and processing of materials like lithium, cobalt, and lead.
-
Weather Dependence (for Solar and Wind): In systems reliant on weather-dependent renewable sources, inconsistent weather can lead to inconsistent power availability.
-
Lower Efficiency in Some Cases: Energy loss can occur during the conversion and storage process, making these systems less efficient than direct grid use in some instances.

While off-grid batteries offer independence and are aligned with renewable energy use, they come with challenges like high initial costs, maintenance needs, and potential limitations in energy availability. The decision to go off-grid should consider these factors along with the specific needs and circumstances of the user.
How To Choose the Best Off-Gird Batteries?
Choosing the best off-grid batteries involves several key factors to consider. Here's a detailed guide to help you make an informed decision:
1. Type of Battery
-
Lead-Acid Batteries: Traditional, cost-effective, but require maintenance (e.g., flooded lead-acid) and have a shorter lifespan.
-
Lithium-Ion Batteries: More expensive, but offer longer life, higher efficiency, and require less maintenance (e.g., LiFePO4).
-
Nickel-Iron Batteries: Very long-lasting and durable, but less efficient and more expensive.
2. Battery Capacity & Power Rating
-
Capacity (measured in kWh): Determines how much energy the battery can store. For off-grid, a higher capacity is generally better.
-
Power Rating (measured in kW): Determines how much power the battery can deliver at a time. A higher power rating is important for running larger appliances.
3. Depth of Discharge (DoD) & Cycle Life
-
DoD: Indicates the percentage of the battery that has been discharged relative to the overall capacity. Batteries with a higher allowable DoD have a longer lifespan.
-
Cycle Life: The number of charge/discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity falls below a certain percentage of the original.
4. Efficiency
-
The efficiency of a battery determines how much of the stored energy can be used. Lithium-ion batteries typically have higher efficiencies (>90%) compared to lead-acid (80-85%).
5. Cost
-
Consider both the upfront cost and the cost over the life of the battery (cost/kWh).
6. Temperature Sensitivity
-
Batteries perform differently in various temperatures. Some may require insulation or cooling systems in extreme climates.
7. Warranty and Lifespan
-
Look for warranties that offer the longest coverage in years and cycles.
8. Compatibility with Existing Systems
-
Ensure the battery is compatible with your inverter and charge controller.
9. Example Calculation:
Suppose you need a system to power a small off-grid cabin that uses 4 kWh per day.
Sizing the Battery: Assuming you want 3 days of autonomy: 4kWh/day * 3days=12kWh
Selecting Battery Type: If choosing LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) for its longevity and efficiency:
-
Example: A 100 Ah 12V LiFePO4 battery gives 1.2 kWh (100 Ah × 12V = 1200 Wh).
-
You would need 10 of these batteries to achieve 12 kWh.
Cost Consideration:
-
If each battery costs $900, the total cost would be $9,000.
Accounting for DoD: If the battery has a DoD of 80%, you need to increase the total capacity to ensure you don’t discharge below this level. Required Capacity=12kWh/0.8=15kWh. You might need a couple more batteries to meet this adjusted requirement.

Final Considerations:
-
Future Expansion: Consider whether you might expand your system.
-
Maintenance: Factor in the maintenance requirements and ease of replacement.
-
Local Regulations: Some areas might have specific regulations regarding battery disposal or installation.
In a nutshell, choosing the right off-grid battery depends on your specific energy needs, budget, and the environmental conditions of your location. Lithium-ion batteries are a popular choice for their efficiency and lifespan, but lead-acid batteries can be more cost-effective for smaller systems or where budget constraints are significant. Always consider the long-term operational costs and not just the upfront investment.
Can Portable Power Stations Function Like Off-Grid Batteries?
Yes, portable power stations can function like off-grid batteries, but with some limitations and differences.
How Portable Power Stations Work?
-
Energy Storage: They store electrical energy in built-in batteries, which can be lithium-ion or other types.
-
Charging: These stations can be charged through AC outlets, solar panels, or sometimes via a car's DC outlet.
-
Power Delivery: They deliver power through various outlets (AC, DC, USB) to charge or run devices like phones, laptops, small appliances, and sometimes even medical equipment(CPAP machines).
Pros of Portable Power Stations
-
Portability: As the name suggests, they are designed for easy transport, making them ideal for camping, road trips, or emergency backup.
-
Eco-Friendly: When charged via solar panels, they offer a green energy solution.
-
Ease of Use: They are generally plug-and-play, requiring minimal setup.
-
Quiet and Safe: They operate silently and don’t emit fumes, unlike gas generators.
Cons of Portable Power Stations
-
Limited Capacity: They have limited energy storage compared to traditional off-grid batteries. This limits their use for long-term or high-power applications.
-
Recharging Time: It can take several hours to recharge, depending on the charging method fully.
-
Cost: High-quality models with larger capacities can be expensive.
-
Dependence on Weather (for Solar Charging): Their efficiency can be compromised on cloudy or rainy days when solar charging.

Comparison to Traditional Off-Grid Batteries
-
Capacity: Traditional off-grid batteries, like deep-cycle batteries, typically have higher capacities and are better suited for long-term energy storage and heavy-duty applications.
-
Installation: Portable power stations are more user-friendly and require less complex installation compared to off-grid battery systems, which often need professional setup and maintenance.
-
Application: Off-grid batteries are ideal for sustained energy supply in remote areas, whereas portable power stations are more suited for temporary, mobile, or emergency power needs.
In summary, portable power stations can function like off-grid batteries for temporary, mobile, or emergency power needs, but they are not as well-suited for long-term, high-capacity energy storage and supply.
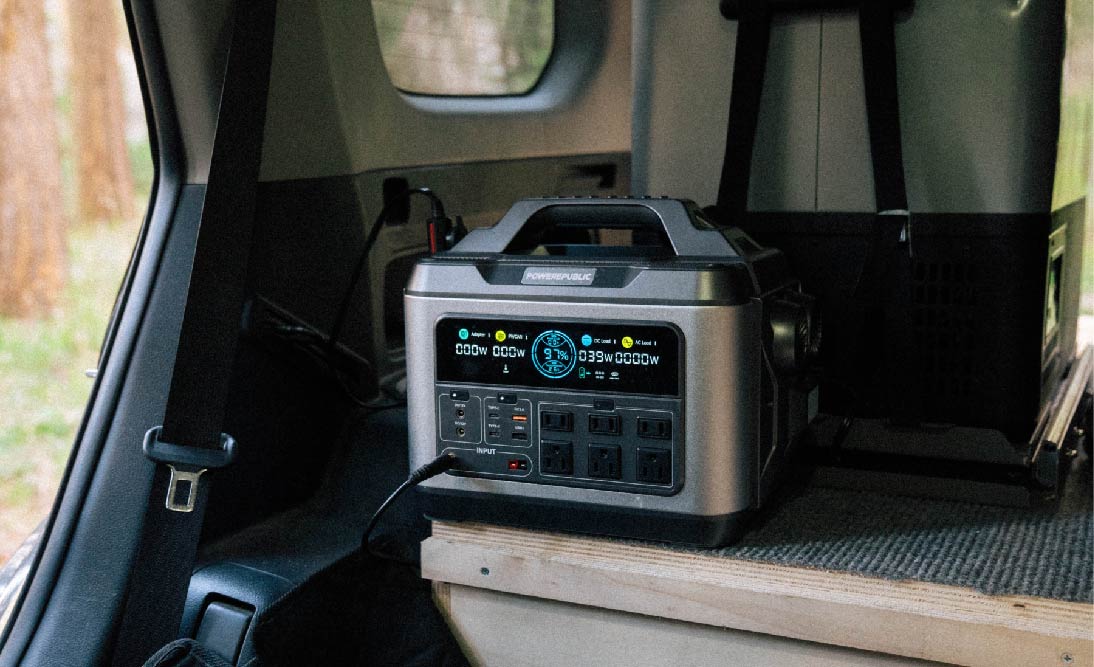
Best Off-Grid Batteries: POWEREPUBLIC Models
From the discussion above, we know that selecting the best off-grid batteries involves considering a multitude of factors and details, and requires professional knowledge to set up the entire system.
For those of you who are looking for a durable, long-lasting, and convenient alternative for temporary, mobile, or emergency power needs, consider the POWEREPUBLIC T1200, T2200, and T3000 portable power stations.

To better understand the functionality of these models, please refer to the table below:
|
Features/Models |
|||
|
Capacity(Wh) |
1110Wh |
2240Wh |
3200Wh |
|
Battery Capacity(mAh) |
50,000mAh |
100,000mAh |
125,000mAh |
|
Running Power |
1200W |
2200W |
3000W |
|
Surge Power |
2600W |
4500W |
6000W |
|
Battery Type |
Lithium-Ion |
LiFePO4 |
LiFePO4 |
|
Output Ports |
13 |
15 |
15 |
|
Charging Methods |
AC Adapter, Solar Panel, Car Charger |
AC Adapter, Solar Panel, Car Charger |
AC Adapter, Solar Panel, Car Charger |
|
Weight |
31Ibs/14Kg |
64Ibs/29Kg |
88Ibs/40Kg |
|
Dimensions(Inch) |
14.3*9.3*10.6 |
18.3*11.8*12.2 |
18.3*11.8*14.5 inch |
|
Suitable For |
Camping & Off-Grid Living |
Off-Gird Living & Home Backup |
Off-Gird Living & Home Backup |
|
Brand Rating |
|||
|
Est.Running Time(h) |
Est.Running Time(h)=Capacity(Wh) * 0.85 / Power of the item(W) |
||
|
TV (100W) |
9.5 hours |
19 hours |
27 hours |
|
LED Light (150W) |
6.3 hours |
12.6 hours |
18 hours |
|
Ceiling Fan (200W) |
4.7 hours |
9.5 hours |
13.5 hours |
|
Wi-Fi Router (250W) |
3.7 hours |
7.6 hours |
10.5 hours |
|
Microwave Oven (800W) |
1.2 hours |
2.4 hours |
3.4 hours |
|
Refrigerator (1000W) |
1 hour |
2 hours |
2.7 hours |
|
Washing Machine (1200W) |
0.7 hours |
1.5 hours |
2.2 hours |
|
Portable Heater (1500W) |
/ |
1.2 hours |
1.8 hours |
|
Electric Grill (2000W) |
/ |
1 hour |
1.3 hours |
|
Air Conditioner (2500W) |
/ |
/ |
1 hour |
Note That:
-
For a clearer understanding of how these devices compare, please visit our Compare page for additional information.
-
Accurate wattage details for each device can be found in their respective user manuals.
-
The provided estimated running times are based on the assumption that only a single device is operated at once and that the power stations are fully charged (at 100% battery capacity).
-
It's important to consider various factors including the present charge level of the power stations, their continuous and peak power capabilities, the number of devices you intend to use simultaneously, and the total power needs of your setup.
FAQ I: What’s the Lifespan of Off-Grid Batteries?
Answer: The lifespan of off-grid batteries varies depending on the type, usage, and maintenance.
For example:
Lead-Acid Batteries: Typically last between 5 to 7 years. If a lead-acid battery is cycled (charged and discharged) daily in an off-grid system, it might reach around 1,800 cycles. For instance, if you use 30% of the battery capacity daily, you can expect it to last around 6 years.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: These can last between 10 to 15 years. Lithium-ion batteries have a higher cycle count, often up to 5,000 cycles or more. For example, if you use 50% of a lithium-ion battery's capacity daily, it could last for over 13 years.

FAQ II: Are Off-Grid Batteries Worth It?
Answer: Off-grid batteries can be worth the investment for energy independence and backup power.
For instance, consider a household that consumes 30 kWh daily. If the local electricity cost is $0.15 per kWh, the daily cost is $4.50. By investing in an off-grid system, let's say with an initial cost of $10,000 for batteries and setup, the system would pay for itself in about 6 years (excluding other system costs like inverters, solar panels, etc.). After this, the energy is essentially free, barring maintenance costs.

FAQ III: What Sized Portable Power Stations Do I Need?
Answer: The size of the portable power station you need depends on your power requirements.
For example:
-
Light Use (e.g., charging phones, running a lamp): A 300W power station can suffice. For instance, charging a smartphone (5W) for 2 hours a day and using an LED lamp (10W) for 5 hours will consume about 70Wh daily.
-
Moderate Use (e.g., powering a fridge, TV): A 1,000W to 2,000W station might be needed. If a fridge uses 1 kWh/day and a TV (100W) is used for 4 hours, the daily consumption is around 1.4 kWh.
-
Heavy Use (e.g., running multiple appliances): You might need a power station of 3,000W or more. Running a fridge (1kWh/day), a microwave oven (800W for 1 hour), and an AC unit (2,500W for 4 hours) would require about 11.8kWh per day.

So it's always good to estimate your power usage and choose a power station with a bit higher capacity than your calculated needs to ensure reliability.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding and choosing the right off-grid batteries is crucial for effective and sustainable energy independence. Off-grid batteries, like those offered by POWEREPUBLIC, provide reliable and efficient power solutions, catering to various needs from temporary mobile setups to full home energy systems. Whether it's for light usage in remote camping trips or heavy-duty applications in off-grid living, selecting the appropriate battery capacity and type is key to maximizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
POWEREPUBLIC's range, including models like the T1200, T2200, and T3000, highlights the versatility and adaptability of modern off-grid battery solutions. These batteries not only ensure a steady power supply but also contribute to a greener, more sustainable energy footprint, making them an ideal choice for those seeking to embrace off-grid living. With careful consideration of factors such as capacity, lifecycle, and specific power needs, users can efficiently harness the benefits of off-grid batteries for a more self-sufficient and environmentally conscious lifestyle.