Table of Contents:
-
Battery Backup Without Solar: POWEREPUBLIC Portable Power Stations
-
FAQ I: Can Portable Power Stations or Solar Generators Power an Entire House?
-
FAQ III: Can I Use a Portable Power Station While Charging it?
Battery backups without solar have emerged as a practical solution for those facing challenges in integrating solar power into their energy systems. Often, constraints like limited sunlight exposure, budget limitations, or spatial restrictions make the use of solar panels impractical or impossible. In such cases, a battery backup without solar becomes a vital resource, providing dependable power in times of need. This is particularly true in urban settings or for renters who may not have the option to install solar panels. Furthermore, the simplicity and lower initial cost of these systems make them an attractive option for emergency power supply, despite their reliance on the grid.
Battery backups without solar, like POWEREPUBLIC portable power stations, offer a convenient and budget-friendly alternative for various applications, from outdoor recreational activities to essential home power during outages. They stand as a testament to the flexibility and efficiency that non-solar emergency power solutions can provide, ensuring continuous power availability even when solar options are not feasible.
In this guide, we are going to talk about everything about battery backup without solar, guide you on how to choose the ideal option, and introduce 3 models from POWEREPULIC for short-term power outages. Hope you will find this guide useful.
Battery Backup Overview
What are Battery Backups?
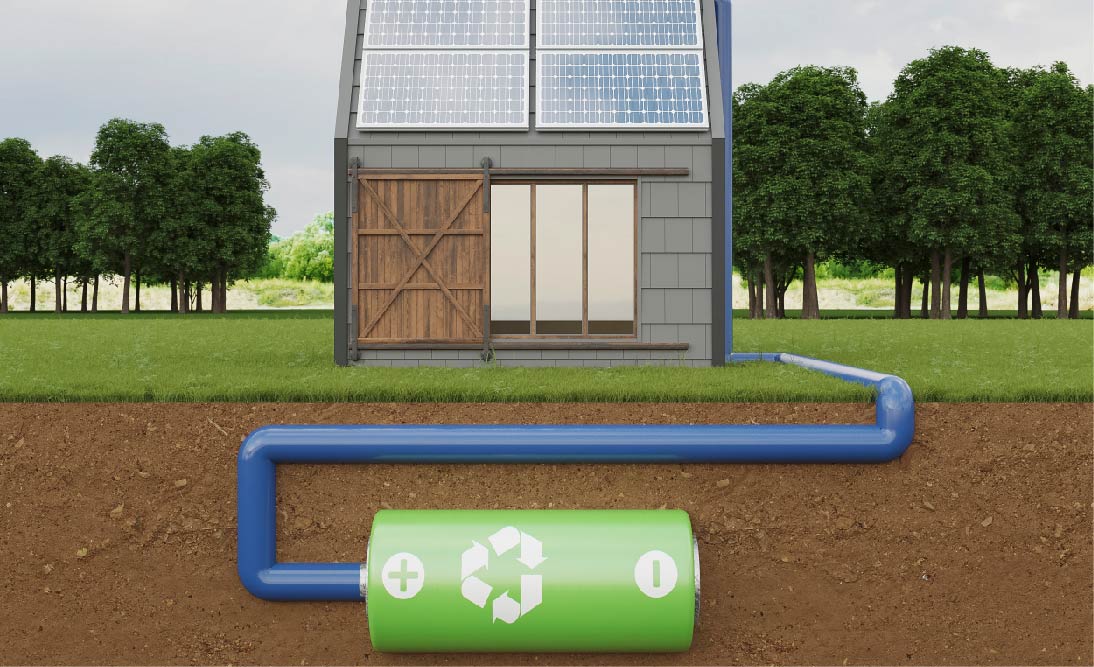
Battery backups, or Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS), are systems designed to provide emergency power when the main power source fails. When integrated with solar panels, these systems not only offer a backup during power outages but also harness renewable energy, providing an eco-friendly and efficient power solution.

Main Components and How They Work
-
Battery: Stores electrical energy for later use. Modern systems often use lithium-ion batteries for their higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
-
Charger: Converts AC power from the grid or DC power from solar panels to recharge the battery. Smart chargers optimize charging rates based on battery condition and solar availability.
-
Inverter: Converts DC power from the battery (and directly from solar panels) into AC power for standard electrical devices. Inverters can vary in efficiency and output quality, with pure sine wave inverters offering the best compatibility for sensitive electronics.
-
Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity. The capacity and efficiency of the panels dictate how much power can be generated and stored.
-
Transfer Switch: Automatically switches the power source from the main grid to the battery in case of an outage, ensuring a seamless transition.
-
Control Unit: Manages the system's operation, including power flow from solar panels, battery charging, and load prioritization.
Price Range
-
Small-scale Home Systems: Can range from $1,000 to $5,000, including a few solar panels, a modest battery bank, and installation.
-
Larger Home or Small Business Systems: Prices range from $5,000 to $20,000, depending on system capacity and sophistication.
-
Commercial-scale Systems: Can exceed $20,000, tailored for extensive power needs and larger facilities.
Applications
-
Residential: Powering essential home appliances during outages and reducing reliance on grid electricity.
-
Commercial: Ensuring uninterrupted business operations, particularly in unstable power grids.
-
Remote Locations: Providing power where grid electricity is unavailable or too costly to install.
-
Sustainable Projects: Reducing carbon footprint and promoting green energy use in various settings.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
-
Renewable Energy Utilization: Reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers electricity bills.
-
Reliability: Offers consistent power during outages, protecting against data loss and equipment damage.
-
Sustainability: Decreases carbon footprint and promotes environmental conservation.
-
Incentives: May be eligible for government rebates and tax incentives.
Cons:
-
Upfront Cost: High initial investment for solar panels, battery storage, and installation.
-
Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance, especially for batteries and solar panels.
-
Space Requirements: Solar panels and battery systems can require significant space.
-
Weather Dependent: Solar panel efficiency is dependent on sunlight availability, affecting power generation.
Examples/Calculations
-
Residential Application: A home system with 5kW solar panels and a 10kWh battery storage can power critical loads like refrigerators, lights, and a small AC unit for several hours. The exact duration depends on usage patterns and sunlight availability.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Assuming an average electricity cost of $0.13 per kWh and a system that offsets 500 kWh per month, the monthly savings would be $65. For a system costing $10,000, the payback period without considering incentives or financing costs would be approximately 12.3 years.
-
Environmental Impact: A 5kW solar system can generate about 7,000 kWh per year in a sunny climate, potentially offsetting nearly 5 tons of CO2 annually compared to coal-generated power.
In short, battery backups integrated with solar panels offer a sustainable and reliable power solution for various applications, from residential to commercial. While the initial costs and maintenance requirements are significant, the benefits of renewable energy utilization, reliability during outages, and potential savings make it an attractive option for many.
Can I Use a Battery Backup Without Solar?
While the integration of battery backups with solar panels has gained popularity, it's entirely possible to use a battery backup without solar. This approach is often necessary in scenarios where solar panel installation is not viable due to various reasons like location, budget, or space constraints. Here, we explore why and how you can use a battery backup without solar, along with key factors to consider and its pros and cons.

Why Use a Battery Backup Without Solar?
-
Limited Sunlight Exposure: In areas with low sunlight or frequent overcast conditions, solar panels may not be efficient.
-
Budget Constraints: The initial cost of setting up a solar system can be prohibitive for some.
-
Space Limitations: Not all properties have the required space or suitable rooftops for solar panel installation.
-
Simplicity: A battery backup without solar offers a more straightforward, less complex system to maintain.
How to Set Up a Battery Backup Without Solar
-
Selecting the Right Battery Backup: Choose a UPS system based on your power needs. For instance, a 1500VA UPS can power a home office setup for a short duration.
-
Installation: Install the system in a location close to the devices it will power, ensuring it's connected to a reliable power source for charging.
-
Testing and Maintenance: Regular testing and maintenance of the battery backup are crucial for ensuring its effectiveness during power outages.
Factors to Consider
-
Power Requirement: Calculate the wattage of the devices you need to support and choose a battery backup with adequate capacity.
-
Backup Duration: Consider how long you need the backup to last. For instance, a 1000W load would require a significantly larger battery to run for several hours compared to a few minutes.
-
Battery Type: Lithium-ion batteries offer longer life and better performance but at a higher cost compared to lead-acid batteries.
Price Range
-
For Basic Home Use: Smaller UPS systems can cost between $50 to $300, suitable for powering a few essential devices.
-
Mid-range Systems: For larger home or office use, prices can range from $300 to $1,000, offering more power and longer backup times.
-
High-capacity Systems: For extensive home use or small businesses, expect to pay between $1,000 and $5,000. These systems offer substantial backup power for multiple devices over a longer period.
Pros and Cons of Battery Backup Without Solar
Pros:
-
Reliability: A battery backup without solar ensures power availability during outages, protecting against data loss and equipment damage.
-
Lower Initial Cost: Eliminating solar panels significantly reduces the upfront investment.
-
Ease of Installation: These systems are generally easier and quicker to set up compared to solar-integrated setups.
-
Flexibility: Can be used in various settings, regardless of solar viability.
Cons:
-
Dependence on Grid: Without solar, the system relies solely on the grid for recharging, which can be problematic in areas with frequent power outages.
-
Operating Costs: The battery backup without solar will increase electricity usage, as it draws power from the grid for charging.
-
Environmental Impact: Lacks the renewable energy aspect of solar, relying on traditional power sources.
Examples/Calculations
-
Cost Analysis: For a typical home UPS system (say, 1500VA/900W), running a PC (300W), a monitor (100W), and some essential lights (100W), the power requirement sums up to 500W. For a battery backup without solar, this setup can offer around 1-2 hours of backup depending on the battery's capacity.
-
Environmental Consideration: Unlike a solar-integrated system, a battery backup without solar doesn't reduce carbon footprint. However, it still provides the reliability needed during power outages.
So, using a battery backup without solar is a viable option for those seeking a reliable emergency power source without the complexities or costs associated with solar panel installation. While it lacks the renewable energy benefits of solar, its ease of use, lower initial cost, and reliability make it an attractive option for many users. The decision to go for a battery backup without solar should be based on individual circumstances, power needs, and environmental considerations.
Battery Backup With Solar Vs. Battery Backup Without Solar
The choice between a battery backup with solar and a battery backup without solar is important. Each has its unique set of advantages and considerations. This comparison aims to elucidate these differences, helping you make an informed decision.

Comparison
|
Factor |
Battery Backup With Solar |
Battery Backup Without Solar |
|
Initial Cost |
High ($5,000 to $20,000+) |
Lower ($50 to $5,000) |
|
Operational Cost |
Lower (solar energy) |
Higher (grid electricity) |
|
Environmental Impact |
Lowers carbon footprint |
Standard grid emissions |
|
Dependency |
Sunlight |
Electrical grid |
|
Installation Complexity |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Long-term Savings |
Significant |
Minimal |
|
Ideal Application |
Sustainable projects, areas with high sunlight exposure |
Areas with limited sunlight, urban settings, renters |
The choice between a battery backup with solar and a battery backup without solar hinges on several factors such as budget, environmental priorities, location, and space availability. Solar-integrated systems offer long-term savings and environmental benefits but come with a higher upfront cost and complexity.
On the other hand, a battery backup without solar provides a more straightforward, budget-friendly solution, albeit with higher operational costs and a greater environmental impact over time. Your specific needs and circumstances will dictate the most suitable option.
How To Select the Ideal Battery Backup Without Solar?
Choosing the ideal battery backup without solar is a significant decision for ensuring uninterrupted power in situations where solar integration isn't feasible or preferred. This section focuses on how to select a battery backup without solar, taking into account various factors and providing examples and calculations for clarity.

Step 1: Assessing Your Power Needs
-
List Essential Devices: Begin by listing the devices you need to operate during a power outage. For example, a home setup might include a refrigerator, a computer, and lighting.
-
Calculate Total Wattage: Add up the wattage of these devices. If a fridge uses 200W, a computer 300W, and lighting 100W, the total load is 600W.
-
Determine Backup Duration: Decide how long you need these devices to run during an outage. If you need them for 2 hours, your battery backup without solar should have enough capacity to provide at least 1200Wh (600W × 2 hours).
Step 2: Selecting the Battery Backup System
-
Choose the Right Capacity: Based on your total wattage and desired backup duration, select a UPS with the required capacity. For the 600W load needing 2 hours of backup, look for a UPS system of at least 1200Wh.
-
Battery Type Considerations: Modern battery backups without solar typically use lithium-ion batteries for their efficiency and longevity, although they may be more expensive than traditional lead-acid batteries.
-
Inverter Specifications: Ensure the inverter in the UPS can handle your calculated load. A pure sine wave inverter is recommended for sensitive electronics.
Step 3: Budgeting and Cost Considerations
-
Estimate Initial Costs: Prices for a battery backup without solar can range from $50 for basic units to $5,000 for high-capacity models. For a medium-sized home system, expect to pay between $300 and $1,000.
-
Operational Costs: Factor in the costs of electricity needed to charge the UPS, though this is usually a minor expense compared to the cost of not having power during outages.
Step 4: Installation and Maintenance
-
Easy Setup: A key advantage of a battery backup without solar is its ease of installation. Most systems are plug-and-play and can be set up without professional help.
-
Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine checks and maintenance, particularly for the battery, to ensure longevity and consistent performance.
Step 5: Environmental Impact
-
While a battery backup without solar doesn’t harness renewable energy, selecting an energy-efficient model can help minimize its environmental impact.
Examples and Calculations
-
Example Scenario: For a home requiring a 600W load for 2 hours, a suitable battery backup without solar would be a UPS rated at least 1200Wh.
-
Cost Calculation: If a suitable UPS costs around $500, and it's used for 20 power outages a year, the cost per outage in the first year (excluding electricity costs) is $25.
Section Wrap-Up
Selecting the ideal battery backup without solar involves a careful analysis of your power needs, budget, and operational conditions. While a battery backup without solar lacks the renewable benefits of solar-integrated systems, it provides a reliable, cost-effective solution for uninterrupted power.
By considering the total power requirements, desired backup duration, budget, and the specific needs of your environment, you can choose a system that offers peace of mind and consistent power support. Remember, the key to selecting the right battery backup without solar is balancing your power requirements with budgetary and environmental considerations.
Battery Backup Without Solar: Portable Power Station
Is a Portable Power Station Feasible as a Battery Backup Without Solar?
Yes, using a portable power station as a battery backup without solar is not only possible but practical. These units store electrical energy in built-in batteries, typically lithium-ion, which can be used when access to the main power grid is unavailable. However, portable power stations are only suitable for short-term power outages. If the energy demand is too high or the power outages last for days, you will need a battery backup system instead.

Applications of Portable Power Stations
-
Outdoor Activities: Perfect for camping, fishing, or any off-grid activities where traditional power sources are inaccessible.
-
Emergency Home Power: Useful for powering essential devices during power outages, like lights, smartphones, and small appliances.
-
Professional Use: Ideal for field work where power needs are temporary and mobility is key, such as for photographers or researchers.
How To Select the Ideal Portable Power Station?
-
Assess Power Requirements: Determine the wattage of devices you'll need to power. Add up their wattages to estimate your total power need.
-
Consider Battery Capacity: Choose a power station with enough capacity to meet your power needs for the desired duration. For example, a 300W device running for 3 hours would need at least 900Wh.
-
Portability: If mobility is a priority, consider the size and weight of the power station.
-
Output Options: Ensure it has the appropriate output ports for your devices (AC, DC, USB, etc.).
-
Recharge Options: Some models can be recharged via AC outlets, cars, or even compatible solar panels.
-
Additional Features: Features like an LCD, carrying handles, and built-in lights can add convenience.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
-
Versatility and Mobility: Can be used in various settings and easily transported.
-
Eco-Friendly: No emissions, making them suitable for indoor use and environmentally friendly.
-
Silent Operation: They operate quietly compared to gas-powered generators.
-
Ease of Use: Often requires minimal setup and maintenance.
Cons:
-
Limited Energy Storage: Can only store a finite amount of energy.
-
Recharging Time: It may take several hours to fully recharge.
-
Cost: High-capacity models can be expensive.
-
Weight: Larger units can be heavy, although they're generally portable.
Price Range
-
Basic Models: $100 to $300, suitable for charging small devices.
-
Mid-Range Models: $300 to $1,000, can power multiple devices for a few hours.
-
High-End Models: $1,000 to $3,000, offer extensive power for larger devices over longer periods.
Examples and Calculations
-
Scenario: You need to power a 40W laptop for 5 hours and a 10W light for 8 hours.
-
Total Power Requirement: (40W x 5h) + (10W x 8h) = 200Wh + 80Wh = 280Wh
-
Choosing a Power Station: A 500Wh portable power station would suffice, offering additional capacity for other small devices or longer usage.
Section Conclusion
Portable power stations are a convenient and efficient form of battery backup without solar, ideal for a range of applications from outdoor recreation to emergency home use. They offer a balance of portability, power capacity, and ease of use, making them a versatile choice for many scenarios. When choosing a portable power station, consider your specific power requirements, portability needs, and budget to find the model that best suits your needs.
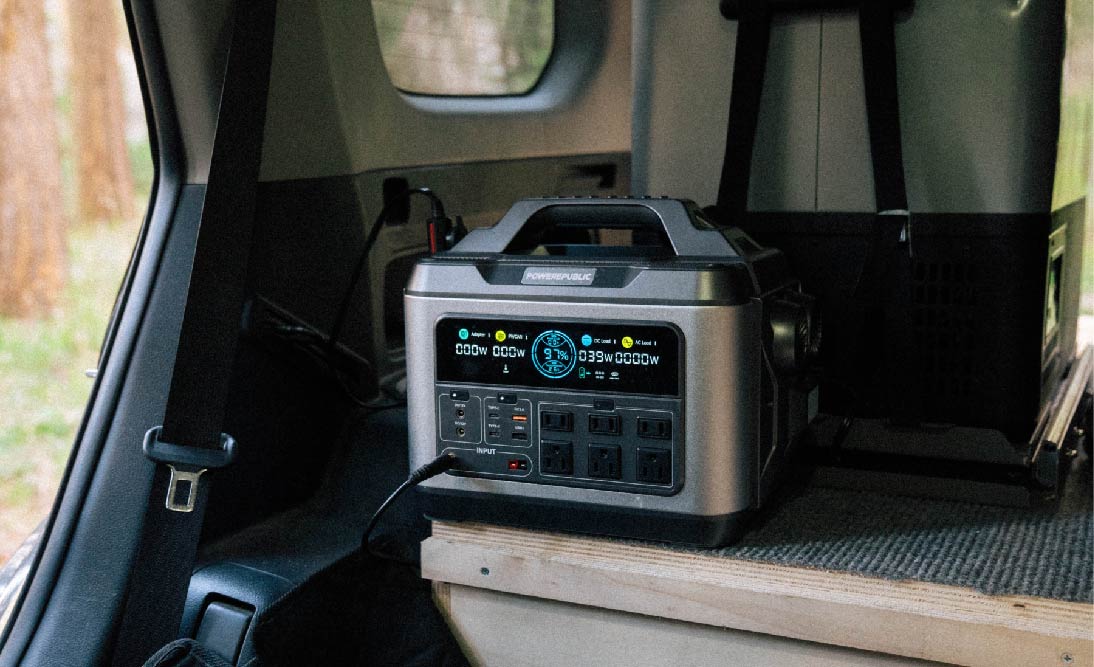
Battery Backup Without Solar: POWEREPUBLIC Portable Power Stations
From the discussion above, we know that portable power stations are a convenient and efficient form of battery backup without solar, ideal for a range of applications from outdoor recreation to emergency home use. They are suitable for short-term power outages and less energy-demanding scenarios.

So, for those of you searching for a battery backup without solar, or a more budget-friendly option, consider choosing POWEREPUBLIC portable power stations. For outdoor usage such as camping, van life, and RV living, we recommend the T1200 model. For both indoor and outdoor usage, we recommend the T2200 model for extended periods. For home battery backup, we suggest the T3000 model. Each model has its features. So, let's take a look at each of them using the table below:
|
Feature/Model |
|||
|
Capacity |
1110Wh/50,000mAh |
2240Wh/100,000mAh |
3200Wh/125,000mAh |
|
Rated Power |
1200W |
2200W |
3000W |
|
Peak Power |
2600W |
4500W |
6000W |
|
Battery Type |
Lithium-Ion(800+ cycles) |
LiFePO4 Batteries(3000+ cycles) |
LiFePO4 Batteries(3000+ cycles) |
|
Number of Ports |
13 Output Ports |
15 Output Ports |
15 Output Ports |
|
Charging |
AC Adapter, Solar Panel, Car Charger |
AC Adapter, Solar Panel, Car Charger |
AC Adapter, Solar Panel, Car Charger |
|
Solar Input |
230W |
230W |
230W |
|
Weight |
31Ibs/14Kg |
64Ibs/30Kg |
88Ibs/40Kg |
|
Dimensions |
14.3*9.3*10.6 Inch |
18.3*11.8*12.2 inch |
18.3*11.8*14.5 inch |
|
POWEREPUBLIC - 4.5 raging on Trustpilot. |
|||
|
Est.Operation Time(h) |
The operation time(h)=Capacity(Wh) * 0.85 / The power of the item(W) |
||
|
TV (100W) |
9.5 hours |
19 hours |
27 hours |
|
Mini Fridge (120W) |
7.5 hours |
15.5 hours |
22.5 hours |
|
Coffee Maker (600W) |
1.5 hours |
3 hours |
4.5 hours |
|
Electric Kettle (800W) |
1.2 hours |
2.4 hours |
3.5 hours |
|
Microwave (1000W) |
1 hour |
2 hours |
2.5 hours |
|
Washing Machine (1500W) |
/ |
1.3 hours |
1.8 hours |
|
Portable Heater (2000W) |
/ |
1 hour |
1.4 hours |
|
Air Conditioner (3000W) |
/ |
/ |
1 hour |
Note That:
-
To facilitate an easier comparison, further details can be found on our Comparison page.
-
The projected usage duration is based on the assumption that only a single appliance is in use at any given time with the battery being fully charged. It's important to remember that the power consumption of devices and appliances may vary depending on the manufacturer.
-
It is essential to verify both the operational and initial surge wattage requirements of your devices, as well as the capacity of the portable power station. Ensure that the combined operational and starting power demand of your device does not exceed the output capacity of the power station.
FAQ I: Can a Portable Power Station or Solar Generator Power an Entire House?
Answer: Portable power stations and solar generators are typically designed for temporary, mobile, or emergency power needs, not for powering an entire house continuously. They are best suited for powering a limited number of appliances or devices simultaneously, especially those with lower energy requirements.

Example Calculation:
Suppose you have a portable power station with a capacity of 1500Wh. If you want to power a refrigerator (200W), a TV (100W), and a few lights (60W combined), the power station can support these for a certain duration.
-
Total Power Consumption: 200W + 100W + 60W = 360W
-
Operational Time: 1500Wh / 360W ≈ 4.17 hours
This shows that while a portable power station can support several essential appliances, it's not feasible to power an entire house, especially with high-demand appliances like air conditioning units, large heaters, or washing machines for extended periods.
FAQ II: What’s the Lifespan of a Portable Power Station?
Answer: The lifespan of a portable power station largely depends on the battery type and the number of charge cycles it can sustain. Most high-quality portable power stations use lithium-ion or lithium-iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries.

-
Lifespan Expectancy: Lithium-ion batteries typically last for about 500 to 1000 charge cycles, whereas LiFePO4 batteries can last for over 2000 charge cycles.
-
In Practice: If you use and recharge your portable power station every other day, a lithium-ion battery could last approximately 3 to 5 years, while a LiFePO4 battery could last well over 5 years.
Regular maintenance and proper usage can also extend the lifespan of your portable power station.
FAQ III: Can I Use a Portable Power Station While Charging it?
Answer: Yes, most modern portable power stations support pass-through charging, meaning you can use them to power devices while they are being charged.

However, there are a few considerations:
-
Charging Efficiency: Using a power station while it’s charging may increase the total time required to fully recharge the battery.
-
Heat Generation: Continuous operation and charging might generate additional heat, so it's important to keep the power station in a well-ventilated area.
-
Battery Health: Frequently using pass-through charging can affect the long-term health and efficiency of the battery, so it's advisable to use this feature sparingly.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the best practices for using your specific portable power station model.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, when seeking a battery backup without solar, understanding the various options available is crucial. Battery backups without solar, such as Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS), offer a reliable source of emergency power. They are particularly useful in areas where solar integration isn’t feasible, providing uninterrupted electricity during outages without the need for solar panels.
For those considering a battery backup without solar, portable power stations like those from POWEREPUBLIC emerge as a budget-friendly and efficient choice. These stations are perfect for short-term power needs, from outdoor activities to emergency home usage. They embody the versatility and convenience that battery backups without solar can offer, especially in scenarios where solar power isn't an option. Ultimately, the selection of a battery backup without solar hinges on individual power needs, environmental considerations, and budget constraints. Whether it's for residential, commercial, or recreational use, battery backups without solar ensure that your power needs are met reliably and efficiently.
Discover more about POWEREPUBLIC as a Battery Backup Without Solar.