Table of Contents:
-
How To Select the Ideal Lithium Battery Banks for Your Energy Needs?
-
FAQ I: What’s the Lifespan of Lithium Battery Banks and Portable Power Stations?
In today's rapidly advancing world, the quest for efficient, reliable, and portable energy solutions leads us to the burgeoning field of lithium battery banks. A common challenge that users often face with these power sources is balancing the need for high energy density, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. Lithium battery banks, known for their exceptional energy efficiency and durability, are revolutionizing how we power everything from small electronic devices to large-scale solar systems and electric vehicles. However, the initial investment for these high-performance batteries can be daunting for many, raising questions about their long-term value and applicability in everyday scenarios.
This blog delves into the intricate world of lithium battery banks, exploring their types, benefits, and considerations to help you determine if they are a worthwhile investment for your specific energy needs. Whether you're considering a portable power station for outdoor adventures or a robust battery bank for your home energy system, understanding the nuances of lithium battery technology is key to making an informed decision. Let's embark on this electrifying journey to unravel the potential of lithium battery banks and their impact on our energy future.
Lithium Battery Banks Overview
What Are Lithium Battery Banks?
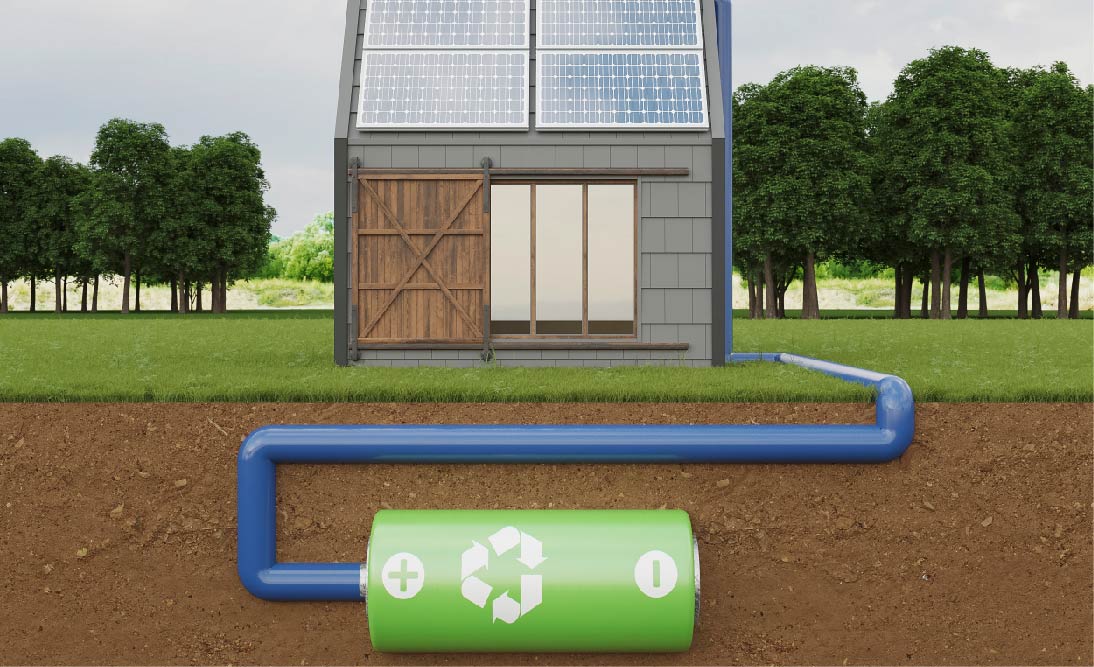
Lithium battery banks are collections of lithium-ion (Li-ion) or lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries linked together to store electrical energy. These batteries are known for their high energy density, long life, and efficiency. They consist of lithium and other materials like cobalt or manganese, which act as cathodes in the batteries.

How Do Lithium Battery Banks Work?
The operation of lithium battery banks is based on the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charge and discharge cycles. During the charging phase, lithium ions travel from the cathode to the anode, resulting in energy storage. In the discharge phase, these ions return to the cathode, releasing energy that powers various devices.
-
During Charging: The anode absorbs lithium ions, leading to the accumulation of energy.
-
During Discharging: The ions revert to the cathode, liberating energy for use by connected devices.
This entire operation is regulated by a Battery Management System (BMS), which plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and extending the lifespan of the battery bank.
Applications of Lithium Battery Banks
Lithium battery banks have a wide range of applications, including:
-
Portable Electronics: These batteries are pivotal in powering smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other personal gadgets.
-
Electric Vehicles (EVs): They serve as the primary power source for electric vehicles, prized for their high energy density and efficiency.
-
Solar Energy Systems: Lithium battery banks are used to store energy in solar panel systems, making solar power more reliable and accessible.
-
Backup Power: They provide emergency power solutions for homes and businesses, ensuring continuity during power outages.
-
Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Boats: Ideal for off-grid living, they offer a dependable power source in mobile environments.
-
Portable Power: Crucial for situations where traditional power sources are unavailable or impractical, lithium battery banks are used in portable power stations, outdoor activities, fieldwork, and emergency power kits.
Price Range of Lithium Battery Banks
The price of lithium battery banks varies widely based on capacity, quality, and application.
-
Small Portable Banks: Used for smartphones and tablets, typically range from $20 to $100.
-
Larger Banks for RVs and Solar Systems: Can range from $200 to over $2,000.
-
EV Battery Packs: These are the most expensive, often costing several thousand dollars.
The initial cost is higher compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, but the longer lifespan and better performance of lithium battery banks can make them more cost-effective in the long run.
Section Conclusion
Lithium battery banks represent a significant advancement in battery technology, offering high efficiency, long life, and versatility in applications ranging from everyday electronics to large-scale energy storage and electric vehicles. While the initial investment can be high, their durability and efficiency often justify the cost.
Types of Lithium Battery Banks
When exploring the world of lithium battery banks, two primary types stand out: Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). Both types have unique characteristics and applications, making them suitable for different needs. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right lithium battery bank for your needs.

Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery Banks
-
Composition and Characteristics: Li-ion batteries are composed of lithium and other materials like cobalt, manganese, or nickel. They are known for their high energy density, which translates to a lightweight and compact size with a substantial power capacity.
-
Applications: Li-ion battery banks are widely used in portable electronics, such as smartphones, laptops, and cameras, due to their lightweight and efficiency. They are also increasingly popular in electric vehicles (EVs) and power tools.
-
Advantages: The high energy density of Li-ion batteries allows for longer use between charges, making them ideal for devices and applications where weight and space are critical factors.
-
Price Range: Small Portable Li-ion Banks- Designed for use with devices like smartphones and tablets, these typically range from approximately $20 to $100, depending on capacity and brand. Medium to Large Li-ion Banks - Used for more demanding applications like power tools or electric bicycles, prices range from $100 to $500. Li-ion Banks for Electric Vehicles (EVs) - These are the most expensive, often ranging from $1,000 to several thousand dollars, depending on the EV's specifications and battery capacity.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery Banks
-
Composition and Characteristics: LiFePO4 batteries, a variant of lithium-ion batteries, utilize lithium iron phosphate in their cathode composition. These batteries are distinguished by their stability, extended lifespan, and enhanced safety features.
-
Applications: LiFePO4 battery banks are commonly used in solar energy systems, RVs, boats, and backup power systems. Their stability and safety make them ideal for applications where battery longevity and reliability are paramount.
-
Advantages: These batteries offer a longer lifecycle, can withstand higher temperatures, and are less prone to thermal runaway, making them safer than standard Li-ion batteries. They also maintain a consistent power output throughout their discharge cycle.
-
Price Range: Small to Medium LiFePO4 Banks - Suitable for applications like portable power stations and smaller solar setups, these can range from around $100 to $500. Large LiFePO4 Banks - Commonly used in RVs, solar energy storage, and marine applications, these can range from $500 to over $2,000, reflecting their higher capacity and durability. Industrial-Scale LiFePO4 Banks - Used in large solar installations and backup power systems, these can cost several thousand dollars, depending on the scale and specifications required.
Section Conclusion
Both Li-ion and LiFePO4 lithium battery banks offer unique advantages, making them suitable for a range of applications. Li-ion is preferred for portable electronics and EVs due to its high energy density, while LiFePO4 is favored in situations requiring stability, safety, and a longer lifespan, such as in solar energy systems and RVs. When choosing a lithium battery bank, consider the specific needs of your application to determine the best type for your requirements.
Are Lithium Battery Banks Worth Purchasing?
Yes, they are worth it!
Lithium battery banks are a valuable investment for many, given their advantages in efficiency, longevity, and versatility. They are particularly beneficial where high energy density and long-term reliability are critical.

Pros of Lithium Battery Banks
-
High Energy Density: Lithium battery banks offer more power with less weight. For example, a lithium battery bank for an EV might weigh around 300 kg and store 85 kWh of energy, while a lead-acid battery of the same capacity would weigh significantly more.
-
Long Lifespan: These batteries can endure thousands of charge cycles. A lithium battery bank can last up to 10 years, whereas a traditional lead-acid battery might need replacement after 3-5 years.
-
Efficiency: They have an energy efficiency of about 95%, compared to 80-85% for lead-acid batteries. This means less energy is lost during charging and discharging.
-
Low Maintenance: Lithium batteries don’t require the regular maintenance that lead-acid batteries do, saving time and money over the battery's life.
Cons of Lithium Battery Banks
-
Higher Initial Cost: A lithium battery bank can be significantly more expensive upfront. For instance, a 100 Ah LiFePO4 battery might cost around $1,000, while a similar capacity lead-acid battery could be around $200.
-
Temperature Sensitivity: They can experience reduced performance in extreme temperatures, necessitating additional management systems in some cases.
-
Safety Concerns: While generally safe, they can pose risks like thermal runaway if not properly managed or if of low quality.
Example Calculation: Cost-Effectiveness
Consider a solar energy system using a lithium battery bank:
-
Initial Cost: $2,000 for a lithium battery bank.
-
Lifespan: 10 years.
-
Cost per Year: $200 ($2,000 / 10 years).
Comparatively, for a lead-acid battery:
-
Initial Cost: $500.
-
Lifespan: 3 years.
-
Cost per Year: $167 ($500 / 3 years).
-
Over 10 Years: $1,670 (replacing the battery approximately every 3 years).
Although the lithium battery bank is more expensive initially, over 10 years, the cost difference narrows significantly, making lithium a more cost-effective option in the long run.
Section Conclusion
Lithium battery banks are a worthwhile investment for those requiring efficient, durable, and high-energy storage solutions. They are particularly beneficial for applications like electric vehicles, solar energy systems, and portable power where long-term reliability and performance are key. The higher upfront cost is offset by their longer lifespan, efficiency, and lower maintenance needs, rendering them cost-effective over time. When considering a lithium battery bank, it’s essential to evaluate specific needs and long-term cost implications to determine the most suitable option.
How To Select the Ideal Lithium Battery Banks for Your Energy Needs?
Choosing the right lithium battery bank for your specific energy needs is crucial to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency. This guide will walk you through the process of selecting the ideal lithium battery bank, with practical examples and calculations to aid your decision.

Understanding Your Energy Requirements
-
Calculate Your Energy Consumption: Begin by assessing the energy requirements of the devices or systems you wish to power. For example, if you're powering a home solar system, sum up the energy consumption of all appliances.
-
Determine Capacity Needs: The capacity of a lithium battery bank is measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or kilowatt-hours (kWh). Calculate the total energy consumption per day and match it with a battery bank that can meet or exceed this requirement.
Choosing the Type of Lithium Battery Bank
-
Lithium-ion (Li-ion): Ideal for portable electronics, EVs, and applications where weight and space are constraints.
-
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4): Best suited for solar energy systems, RVs, and applications requiring longevity and safety.
Example Calculation for Solar System:
-
Daily Energy Consumption: 5 kWh.
-
Required Battery Capacity: A LiFePO4 battery bank with a capacity slightly higher than 5 kWh, considering efficiency losses and days with less sunlight.
-
Calculation: If opting for a 6 kWh LiFePO4 battery bank at 80% depth of discharge (DoD), the effective capacity is 4.8 kWh (6 kWh * 0.80), which meets the daily requirement.
Assessing Budget and Long-Term Value
-
Initial Investment vs. Longevity: Compare the upfront cost with the expected lifespan. LiFePO4 batteries may have a higher initial cost but offer a longer lifespan, reducing the overall cost per year.
-
Example: A $2,000 LiFePO4 battery bank with a 10-year lifespan costs $200 per year, whereas a $1,000 Li-ion battery with a 5-year lifespan costs $200 per year as well.
Considering Additional Factors
-
Size and Weight: Li-ion batteries are more compact for space-limited situations.
-
Temperature Tolerance: LiFePO4 batteries perform better in extreme temperatures.
-
Safety: Choose batteries with a robust Battery Management System (BMS).
-
Solar Panel Compatibility: Ensure the battery bank's voltage and capacity are compatible with your solar panel system. The battery should efficiently store and release the solar energy captured. For instance, a 12V solar panel system pairs well with a 12V lithium battery bank.
Section Conclusion
Selecting the ideal lithium battery bank for your energy needs involves understanding your power requirements, choosing the right type of battery, considering budget constraints, and factoring in size, weight, temperature tolerance, and safety. By carefully evaluating these aspects and using the provided examples and calculations as a guide, you can make an informed decision that balances performance with cost-effectiveness.
Can Portable Power Stations Count as Lithium Battery Banks?
Yes, Portable Power Stations are a Form of Lithium Battery Banks.
Portable power stations are indeed a type of lithium battery bank. They are essentially self-contained units that store electrical energy using lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries and can be used similarly to traditional lithium battery banks.

Portable Power Stations vs. Traditional Lithium Battery Banks
-
Composition: Both use lithium-based batteries, but portable power stations are often designed as all-in-one units with built-in inverters and multiple outlets.
-
Portability: Portable power stations are designed for mobility, whereas traditional lithium battery banks are often larger and used in stationary applications.
-
Capacity and Power Output: Traditional lithium battery banks generally offer higher capacity and power output compared to portable power stations.
Pros of Portable Power Stations
-
Mobility: Their compact size and portability make them ideal for outdoor use and emergencies.
-
Versatility: Equipped with various outlets, they can power multiple devices simultaneously.
-
User-Friendly: They often require minimal setup and are easy to use.
Cons of Portable Power Stations
-
Limited Capacity: They typically have less capacity and power output compared to larger lithium battery banks.
-
Higher Cost per Capacity: Portable power stations can be more expensive per watt-hour of capacity.
-
Durability Concerns: Some models may not be as durable as stationary lithium battery banks designed for long-term use.
Price Range of Portable Power Stations
-
Low Capacity (Below 300Wh): Ranging from about $100 to $300, suitable for charging small devices.
-
Medium Capacity (300Wh to 1,000Wh): Priced between $300 and $1,000, ideal for longer trips and more demanding power needs.
-
High Capacity (Above 1,000Wh): These can exceed $1,000, catering to more intensive power requirements.
Section Conclusion
Portable power stations can be classified as a specialized form of lithium battery banks. They offer the convenience of portability and versatility but usually at a higher cost and with less capacity than traditional lithium battery banks. When deciding between the two, consider your specific needs regarding mobility, capacity, power output, and budget. Portable power stations are excellent for on-the-go power and ease of use, while traditional lithium battery banks are better suited for higher-capacity, stationary energy storage needs.
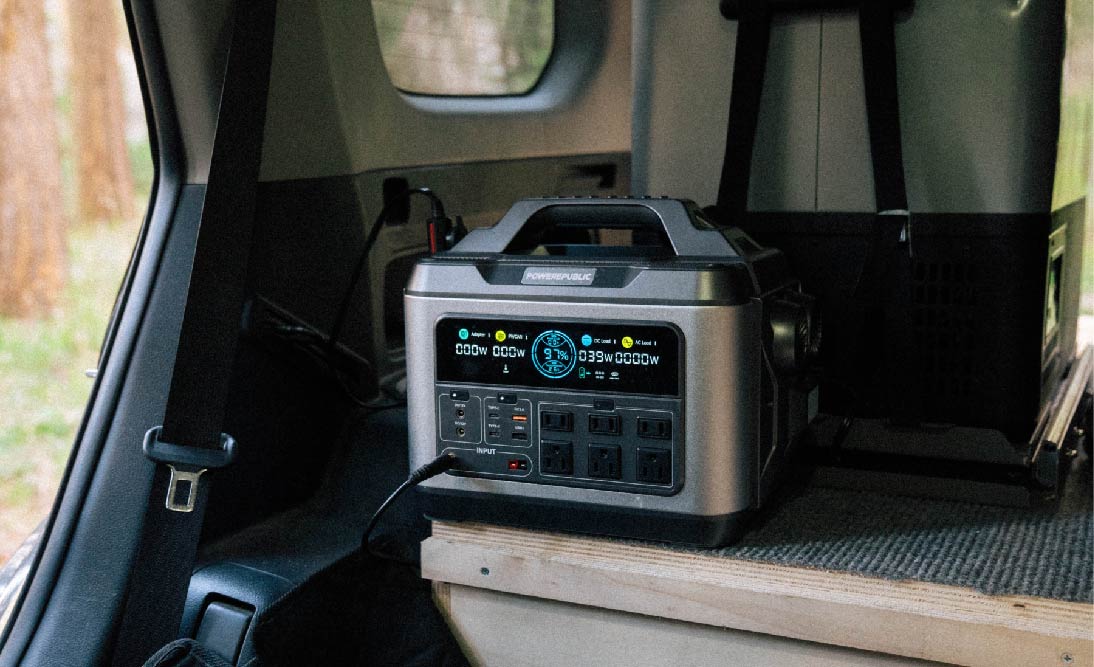
Lithium Battery Banks: POWEREPUBLIC Portable Power Stations
From the section above, we know that portable power stations can be classified as a specialized form of lithium battery banks as they are excellent for on-the-go power and ease of use.
So for those looking for alternative options like this, consider POWEREPUBLIC portable power stations. They are durable, long-lasting, versatile, and powerful for devices and home appliances and can be used for different scenarios and conditions.
-
Low Capacity (Below 300Wh): The T306 model(296Wh/300W), is suitable for charging small devices.
-
Medium Capacity (300Wh to 1,000Wh): The T1200 model(1110Wh/1200W), is ideal for longer trips and more demanding power needs.
-
High Capacity (Above 1,000Wh): The T2200(2240Wh/2200W) and T3000(3200Wh/3000W) models, catering to more intensive power requirements.

To better understand the functionality of these models, please refer to the table below:
|
Features/Models |
||||
|
Capacity(Wh) |
296Wh |
1110Wh |
2240Wh |
3200Wh |
|
Battery Capacity(mAh) |
20,000mAh |
50,000mAh |
100,000mAh |
125,000mAh |
|
Running Power |
300W |
1200W |
2200W |
3000W |
|
Peak Power |
600W |
2600W |
4500W |
6000W |
|
Battery Type |
Lithium-Ion |
Lithium-Ion |
LiFePO4 |
LiFePO4 |
|
Output Ports |
10 Ports |
13 Ports |
15 Ports |
15 Ports |
|
Input Ports |
AC, Solar, Car Socket |
AC, Solar, Car Socket |
AC, Solar, Car Socket |
AC, Solar, Car Socket |
|
Portability |
9.2Ibs/4Kg |
31Ibs/14Kg |
64Ibs/29Kg |
88Ibs/40Kg |
|
Measurements |
11.2*6.1*8.0 |
14.3*9.3*10.6 |
18.3*11.8*12.2 |
18.3*11.8*14.5 |
|
Scenarios |
Charging Essential Devices |
Longer Trips with More Demaning Power |
More Intensive Power Needs |
More Intensive Power Needs |
|
Brand Reviews & Rating |
||||
|
Est. Running Time(h) |
Est.Running Time(h)=Capacity(Wh) * 0.85 / Power of the item(W) |
|||
|
LCD TV (100W) |
2.5 hours |
9.5 hours |
19 hours |
27 hours |
|
Refrigerator (300W) |
0.8 hours |
3 hours |
6.3 hours |
9 hours |
|
Washing Machine (500W) |
/ |
1.8 hours |
3.8 hours |
5.5 hours |
|
Blender (500W) |
/ |
1.8 hours |
3.8 hours |
5.5 hours |
|
Coffee Maker (800W) |
/ |
1.2 hours |
2.3 hours |
3.4 hours |
|
Microwave Oven (1500W) |
/ |
/ |
1.3 hours |
1.8 hours |
|
Portable Heater (1800W) |
/ |
/ |
1.1 hours |
1.5 hours |
|
Hair Dryer (2000W) |
/ |
/ |
1 hour |
1.3 hours |
Note That:
-
Visit our Compare page for more product details.
-
The actual wattage of the items is varied and can be found in their respective user manuals.
-
The estimated running times are calculated based on the assumption that only a single device is running and the portable power station is at 100% battery capacity.
-
Remember to check the continuous and peak power of the devices and appliances. Make sure the highest peak power of your items does not exceed the peak power of the portable power station for successful operation.
FAQ I: What’s the Lifespan of Lithium Battery Banks and Portable Power Stations?
Answer: The lifespan of lithium battery banks and portable power stations largely depends on their battery type and usage patterns. Typically:
-
Lithium-Ion Battery Banks: They can last anywhere from 500 to 1,500 charge cycles. Assuming a full charge-discharge cycle per day, this translates to about 1.5 to 4 years of lifespan.
-
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery Banks: These often last longer, with up to 2,000 to 5,000 charge cycles, equating to about 5 to 14 years of usage.
-
Portable Power Stations: Their lifespan aligns with the type of lithium battery used. A portable power station with a LiFePO4 battery might last longer than one with a standard lithium-ion battery.

Example Calculation:
-
For a LiFePO4 portable power station used every day (1 cycle per day), with 2,000 charge cycles:
-
Lifespan = 2,000 cycles / 365 days per year = approximately 5.5 years
FAQ II: How To Choose The Ideal Portable Power Stations?
Answer: When choosing a portable power station, consider:
-
Capacity Requirements: Calculate your energy needs in watt-hours (Wh). Sum up the wattage of devices you plan to power and estimate how long you'll use them.
-
Portability vs. Power: Balance the need for portability (weight and size) with your required power and capacity.
-
Output Ports Needed: Ensure it has the necessary output types (USB, AC, DC) for your devices.
-
Battery Type: Opt for LiFePO4 for a longer lifespan or standard lithium-ion for cost-effectiveness.
-
Budget: Match your budget with the features and capacity you need.

Example: If you need to power a 500W blender for 2 hours, you'll need at least a 1000Wh capacity (500W * 2 hours).
FAQ III: Can Portable Power Stations Run a House?
Answer: Portable power stations can power certain appliances in a house, but their capacity to run an entire house is limited.

They are ideal for:
-
Emergency Power: Running essential devices like lights, a fridge, a TV, and charging phones during a power outage.
-
Off-Grid Power: Suitable for camping or RVs, where power needs are limited.
However, they might not be sufficient for:
-
High-power appliances: Like central air conditioning, large electric heaters, or entire home systems simultaneously.
-
Long-Term Power Outage: Unless they have a very high capacity or are used sparingly.
Example: A 3000Wh portable power station could run a refrigerator (300W) for about 10 hours (3000Wh / 300W), but might not sustain a whole-house air conditioning system.
Remember, the key is to match your specific power needs with the capacity and capabilities of the portable power station.
Final Thoughts On Lithium Battery Banks
In a nutshell, lithium battery banks stand as a significant innovation. Renowned for their high energy density, longevity, and efficiency, these battery banks are reshaping how we power our daily lives and larger systems alike. Lithium battery banks offer a versatile and durable solution, from powering small electronic devices to being the energy backbone for electric vehicles and solar systems. While their upfront cost may be higher than traditional options, their long-term efficiency and lower maintenance needs make them a worthwhile investment.
For those seeking a mobile and user-friendly alternative, POWEREPUBLIC portable power stations present an excellent option. These stations embody the core advantages of lithium battery banks, catering to on-the-go power needs with various models to suit different scenarios. Embracing lithium battery banks represents a smart step towards a more efficient and reliable energy future.
Discover more about POWEREPUBLIC Portable Power Stations!