Table Of Contents:
-
How to choose the ideal emergency electricity source for your needs?
-
POWEREPUBLIC solar generator kits as emergency electricity sources
Living in big cities like New York often means having reliable power and less extreme weather. But in places like California, Texas, and Florida, the story is different. These states deal with more power outages and severe weather due to where they're located and the climate they face. That's why having a good emergency electricity source is a real game-changer. It can keep you going for hours during a blackout until the regular power comes back on.
In this article, we're going to explain all about emergency electricity sources. We hope it gives you helpful insights after you're done reading.
Let's dive in!
What’s The Definition Of Emergency Electricity Sources?

An emergency electricity source, often referred to as a backup power source or emergency power solution, is a system or device designed to provide electrical power during situations when the primary power source, such as the grid, fails or experiences an outage. These backup sources ensure a continuous supply of electricity, which can be crucial for various purposes, including maintaining essential functions in homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure. Having a reliable power source is crucial to keep all your devices and appliances charged during power outages.
Common Types of Emergency Electricity Sources

When it comes to emergency electricity sources, there are several options. These backup power sources serve as lifelines in times of need, providing power for critical appliances, communication devices, and essential systems, allowing you to maintain comfort, safety, and functionality when the grid fails. Each option offers its own set of advantages and limitations, making it essential to choose the most suitable solution based on your specific needs, location, and circumstances.
Let’s take a look at some common types of emergency power solutions:
1. Portable Generators
Portable generators are small, combustion engine-powered devices that generate electricity. They can be fueled by gasoline, propane, or diesel and typically have outlets for connecting appliances or extension cords.
Use Scenarios: Portable generators are versatile and useful in various situations, such as:
-
Power outages during storms or natural disasters.
-
Providing electricity for camping, tailgating, or outdoor events.
-
Supplying power to construction sites in remote locations.
2. Standby Generators
Standby generators are permanent backup power systems that are installed outside of a home or business. They are connected to the building's electrical system and often run on natural gas or propane. They automatically start when a power outage is detected.
Use Scenarios: Standby generators are ideal for scenarios where uninterrupted power is critical, such as:
-
Homes, particularly in areas with frequent or extended power outages.
-
Businesses, including restaurants and healthcare facilities.
-
Critical infrastructure like hospitals and data centers.
3. Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems consist of solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity. The generated electricity can be used directly or stored in batteries for later use. They are often connected to the grid and can reduce reliance on utility power.
Use Scenarios: Solar power systems are employed for a variety of purposes, including:
-
Off-grid living in remote areas without access to conventional power sources.
-
Reducing electricity bills and promoting sustainability in residential homes.
-
Providing clean, renewable energy for both residential and commercial properties.
4. Portable Power Stations / Solar Generators
Portable power stations, often referred to as solar generators, are compact and battery-based units that store electricity from solar panels or can be charged from the grid. They come with various outlets and often have a pure sine wave inverter for powering appliances and devices.
Use Scenarios: Portable power stations are versatile and can be used in many situations, including:
-
Outdoor Activities: Providing power for camping, hiking, or RV trips without the need for noisy generators.
-
Emergency Preparedness: Offering a clean and silent power source during power outages for essential appliances and medical equipment.
-
Off-Grid Living: Supporting off-grid homes or cabins with a sustainable energy source, especially when paired with solar panels.
-
Remote Work: Ensuring uninterrupted work from anywhere, as they can power laptops, routers, and other devices.
-
Outdoor Events: Supplying electricity for tailgating, outdoor parties, or film screenings.
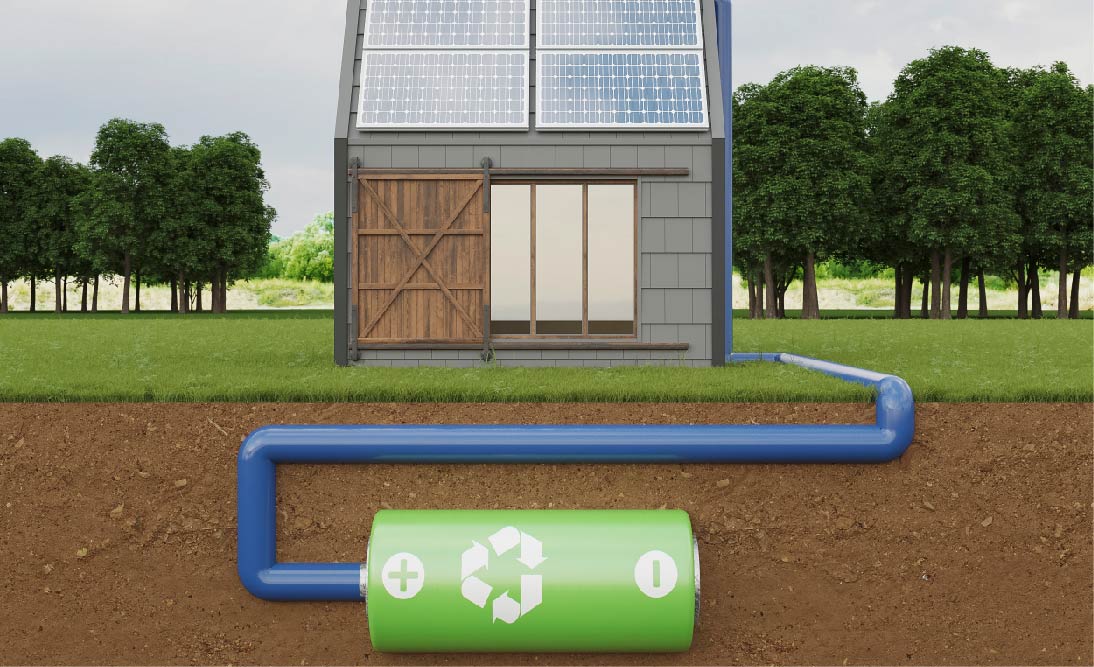
5. Battery Backup Systems
Battery backup systems store electricity in batteries when the grid is operational. During power outages, the batteries supply the stored energy to connected devices, ensuring uninterrupted power for critical applications.
Use Scenarios: Battery backup systems are deployed in situations where continuous power is essential, such as:
-
Homes and businesses to keep essential appliances and equipment running during outages.
-
Storing surplus energy from solar panels for use at night or during cloudy days.
-
Safeguarding sensitive electronic devices against power fluctuations.
6. Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
UPS units are battery-based devices that provide immediate backup power during brief outages. They are designed to protect sensitive electronics like computers, servers, and networking equipment from data loss and damage.
Use Scenarios: UPS units are commonly used in settings where data integrity and uninterrupted operation are critical, including:
-
Home offices and small businesses with vital computing equipment.
-
Data centers and server rooms to maintain server uptime.
-
Supporting gaming consoles and entertainment systems to prevent data loss and sudden shutdowns.
7. Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are renewable energy systems that convert kinetic energy from the wind into electricity. They consist of rotor blades connected to a generator that produces electrical power.
Use Scenarios: Wind turbines are typically deployed in areas with consistent wind resources, such as:
-
Off-grid locations where reliable wind patterns can provide a continuous power source.
-
Homes, farms, or businesses aiming to generate their renewable energy.
-
Communities and regions with access to consistent wind resources for sustainable power generation.
What Are The Pros and Cons Of Emergency Electricity Sources?

These emergency electricity sources(backup power sources) have their strengths and weaknesses, suited for different situations. We've included prices, pros, and cons for each type to make it easier for you to choose the right emergency power solution based on your needs:
|
Sources |
Price Range |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Portable Generators |
$200 - $3,000+ |
|
|
|
Standby Generators |
$5,000 - $20,000+ |
|
|
|
Solar Power Systems |
$3,000 - $15,000+ |
|
|
|
Battery Backup Systems |
$500 - $5,000+ |
|
|
|
$50 - $1,000+ |
|
|
|
|
Wind Turbines |
$4,000 - $30,000+ |
|
|
|
Portable Power Station / Solar Generator |
$200 - $2,000+ |
|
|
Please note that the prices can vary widely, and the pros and cons listed are general examples. Be sure to research specific models and consider your unique needs and circumstances when choosing an emergency electricity source(backup power source). Having reliable power sources is very important to help you get through the “dark” moments.
How to Choose The Ideal Emergency Electricity Source?

Choosing the ideal emergency electricity source(backup power source) begins with a comprehensive assessment of your specific needs and circumstances. To make an informed decision, consider the following factors, starting with the most critical aspects:
1. Power Needs
-
Identifying Critical Loads: Start by listing the appliances and devices that are essential during an outage. This typically includes items like refrigerators, freezers, medical equipment, lights, heating/cooling systems, and communication devices.
-
Wattage Calculation: Determine the power consumption (in watts) of each essential load. You can usually find this information on the appliance's label or in the owner's manual.
-
Total Wattage Requirement: Calculate the total wattage requirement by adding up the power consumption of all the essential loads you need to run simultaneously during an outage. Consider both the running (continuous) wattage and the starting (surge) wattage, as some appliances require more power to start.
-
Prioritization: If the total wattage exceeds the capacity of the emergency electricity source you're considering, prioritize the most critical loads that must be powered during an outage.
2. Capacity
-
Choosing the Right Size: Ensure that the emergency electricity source you select can meet your total wattage requirement. Look for a generator or system that provides sufficient wattage without overloading it.
-
Sizing Generators: Generators are typically rated in watts. Select a generator with a wattage capacity that comfortably exceeds your calculated total wattage requirement to accommodate any surges.
-
Battery Capacity: If you opt for a battery backup system, check the capacity of the battery in ampere-hours (Ah) or kilowatt-hours (kWh). Ensure it can provide adequate power for the necessary duration.
3. Budget
-
Initial Purchase Cost: Consider the upfront cost of the emergency electricity source itself. This includes the cost of the generator, battery system, solar panels, or any other necessary equipment.
-
Installation Costs: Account for any installation expenses, such as hiring an electrician, setting up a transfer switch, or integrating the system with your electrical panel.
-
Operating Costs: Include ongoing expenses, such as fuel (for generators), maintenance, and repairs in your budget. These costs can vary significantly depending on the type of emergency electricity source you choose.
4. Use Frequency
-
Frequency of Outages: Consider how often power outages occur in your area. If you experience frequent outages, it may be worthwhile to invest in a more automated, higher-capacity solution.
-
Temporary vs. Permanent Solutions: If outages are infrequent, you may opt for a more portable or temporary solution that can be stored and used as needed.
5. Environmental Impact
-
Emissions: Gasoline and diesel generators produce emissions, which can contribute to air pollution. Consider cleaner alternatives like natural gas, propane, or solar power to minimize environmental impact.
-
Noise Pollution: Traditional generators can be noisy, potentially causing noise pollution. Solar and battery systems operate silently, making them a quieter and more eco-friendly option.
6. Maintenance and Reliability
-
Regular Maintenance: Generators require regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter replacement, and spark plug checks. Solar panels and batteries typically require less maintenance.
-
Reliability: Choose well-known, reputable brands and models that are known for their reliability and performance during outages.
7. Safety Features
-
Automatic Shutdown: Modern generators often have automatic shutdown features for low oil levels, overloading, or other issues to prevent damage and enhance safety.
-
Carbon Monoxide Detection/Shutoff: Generators emit carbon monoxide; models with built-in detectors and shutoff mechanisms provide added safety.
-
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI): Electrical systems may include GFCIs that prevent shocks by shutting off power in the event of a fault.
-
Weatherproofing: Ensure generators installed outdoors are properly weatherproofed to prevent damage from exposure to the elements.
-
Compliance with Standards: Verify that your chosen emergency electricity source complies with safety standards and certifications, such as UL or CSA.
There are a few other factors to consider but the above ones are the most crucial. Balancing these considerations, along with your specific needs and preferences, will help you select the ideal emergency power solutions that best fit your situation and ensure you have reliable power sources during outages or emergencies.
POWEREPUBLIC Solar Generator Kits For Emergencies

POWEREPUBLIC offers reliable portable power stations and highly efficient portable solar panels. When paired together, they create solar generator kits that can be used as emergency electricity sources(backup power sources) during power outages. You can also use them for outdoor activities like camping and off-grid living.
To help you better understand the functionality of our solar generator kits as emergency power solutions and to compare each of them, we have created the following table for your convenience:
|
Model |
Specifications |
Use Scenario |
Working Time |
|
Power Output: 300W, Surge 600W Battery Capacity: 296Wh Battery Type: Lithium-ion with 800+ cycles to 80% Weight: 9.2Ibs/4Kg Dimension: 11.2*6.1*8.0 inch Output: 10 output ports Solar Input: 120W Max. |
The T306 is compact and portable, making it ideal for short-term and lightweight power needs. It's suitable for:
|
LED light bulb(10-15W): 16 - 25hrs Laptop(30-60W): 4 - 8hrs Smartphone(5-10W): 25 - 50hrs Small fan(20-50W): 5 - 12.5hrs CPAP machine( 30-60W): 4 - hrs DSLR battery(20-40W): 6 - 12.5hrs Portable refrigerator(40-60W): 4 - 6hrs |
|
|
Power Output: 1200W, Surge 2600W Battery Capacity: 1110Wh Battery Type: Lithium-ion with 800+ cycles to 80% Weight: 31Ibs/14Kg Dimension: 14.3*9.3*10.6 Inch Output: 13 output ports Solar Input: 220W Max. |
The T1200 offers a balance between power and portability, suitable for various scenarios:
|
LED TV(80-150W): 6 - 11.5hrs Microwaveoven(600-1200W): 0.5 - 1.5hrs Desktop computer(400-800W): 1 - 2hrs Coffee maker(800-1200W): 0.5 - 1hr Window air conditioner (800-1200W): 0.5 - 1hr Electric kettle(1200-1500W): 0.5 hrs Space heater (1000-1500W): 0.5 - 1hr |
|
|
Power Output: 2200W, Surge 4500W Battery Capacity: 2240Wh Battery Type: LiFePO4 with 3000+ cycles to 80% Weight: 64 Ibs/29Kg Dimension: 18.3*11.8*12.2 inch Output: 15 output ports Solar Input: 220W Max. |
The T2200 is designed for more demanding scenarios where extended power is needed:
|
Refrigerator(100-800W): 2 - 19hrs Chest freezer(100-800W): 2 - 19hrs Washing machine(500-1500W): 1 - 3.5hrs Electric grill(1500-1800W): 1 - 1.2hrs Power tools (1000-2000W): 1 - 2hrs Air compressor(1500-2200W): 0.5 - 1.2hrs Central heating system (1500-2200W): 0.5 - 1.2hrs |
|
|
Power Output: 3000W, Surge 6000W Battery Capacity: 3200Wh Battery Type: LiFePO4 with 3000+ cycles to 80% Weight: 88 Ibs/40Kg Dimension: 18.3*11.8*14.5 inch Output: 15 output ports Solar Input: 220W Max. |
The T3000 is a heavy-duty solution designed for substantial power needs and extended durations:
|
Refrigerator (800-1500W): 1.5 - 3.4hrs Electric oven(1000-5000W): 0.5 - 2.5hrs Water heater(3000-4500W): 0.5 - 1hr Central air conditioner (2000-3500W): 0.5 - 1.3hrs Electric stove(2000-4500W): 0.5 - 1.3hrs Power tools(2000-5000W): 0.5 - 1.3hrs |
Please note that the wattage of the above appliances and devices is just an estimate. If you need a more accurate estimate, you can determine the wattage of the items and use the following formula:
-
Working time (hours) = Capacity of the portable power station (Wh) * 0.85 (conversion rate) / Power of your items (W)
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, selecting the ideal emergency electricity source necessitates a thorough assessment considering power needs, capacity, budget, frequency of use, environmental impact, maintenance, reliability, and safety features. Each emergency power solution—portable generators, standby generators, solar power systems, battery backup systems, UPS units, and wind turbines—comes with distinct advantages and limitations, tailored for various scenarios and locations.
Furthermore, the comparison of POWEREPUBLIC's Solar Generator Kits showcases their diverse applications and estimated working times for different devices. Understanding the power requirements and use scenarios allows for a tailored choice to ensure an uninterrupted power supply during outages or emergencies. Careful consideration of specific needs, environmental impact, and safety features aligns with making a well-informed decision when selecting an emergency electricity source.