Table Of Contents:
In an age where environmental awareness is on the rise, the combination of solar energy and electric vehicles (EVs), exemplified by brands like Tesla, has emerged as a compelling avenue for sustainable living and combating climate change effectively.
Solar panels stand as potent generators of clean, renewable energy, aligning perfectly with the zero-tailpipe emission principle of EVs. Together, they contribute to a decreased reliance on fossil fuels and the mitigation of their associated environmental impacts. However, the seamless integration of EVs with solar charging systems presents its own set of challenges.
Against the backdrop of this potential synergy, a significant portion of electric cars still indirectly rely on fossil fuels. As of 2021, approximately 60% of the United States' electricity was generated from gas and coal sources, while only about 20% came from renewable alternatives such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. This reality introduces complexities into the seemingly straightforward equation of charging EVs.
It's important to recognize that while the conventional charging infrastructure may not eliminate fossil fuel consumption, there's an opportunity for electric vehicle owners to tangibly reduce their carbon footprint. By leveraging solar power systems, EV users can partially supply their vehicle's energy needs through a cleaner energy source.
While solar panels have the potential to meet the energy demands of households, the energy requirements for charging an EV tend to be notably higher. The concept of charging an EV through solar panels is attainable, but it necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of several critical factors before achieving a successful symbiosis between the two technologies.
Charging Your EV With Solar Energy, Doable?
Absolutely. The prospect of charging an electric car through solar energy is viable and stands as an ecologically sound and sustainable method for powering EVs.
To enable the charging of your EV with solar power at your residence, installing a solar panel array along with a suitably capable system balance is a prerequisite. This arrangement ensures sufficient electricity generation for your EV's charging needs.
The question of whether an EV charging station is a necessity arises. While it's not an absolute requirement, incorporating an EV charging station can enhance the efficiency of the charging process. Diverse charging station options exist, categorized as Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3:
Level 1 charging stations utilize a standard 120-volt household electrical outlet. Although all EVs have a plug compatible with regular wall outlets, this method might require extended hours to achieve a full charge.
Level 2 charging stations operate with a 240-volt outlet, resulting in a faster charging rate. However, this option typically involves additional wiring and components installation.
Level 3 DC fast charging stations, capable of charging a car in about 30 minutes, rely on a 480-volt connection. Their installation is costly and complex, making them rare in residential settings.
If your property boasts a solar power system and a compatible charging station, the electricity generated by your solar panels can seamlessly recharge your EV, solidifying the harmonious integration of renewable energy into your driving experience.
Charging Your EV With Portable Solar Panels, Doable?

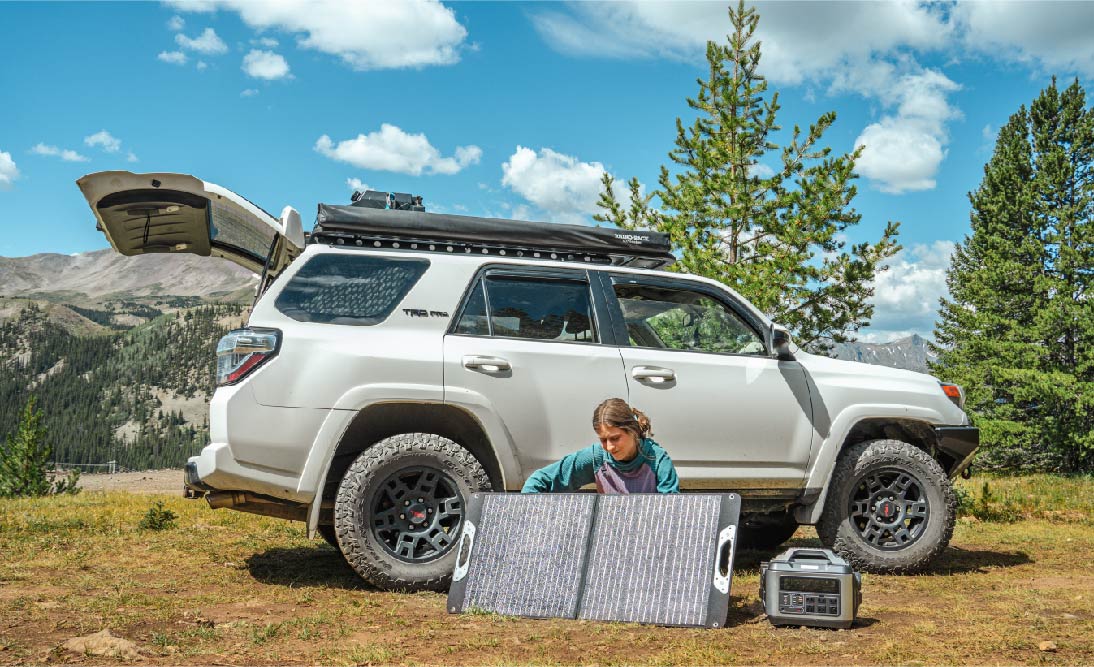
Indeed, the charging capability of solar panels for electric vehicles (EVs) is determined by various factors. Whether the solar panels are portable or fixed in nature does not impact their potential to charge an EV. As long as the photovoltaic (PV) panels deliver sufficient power output, portable solar panels can effectively generate electricity to charge an EV.
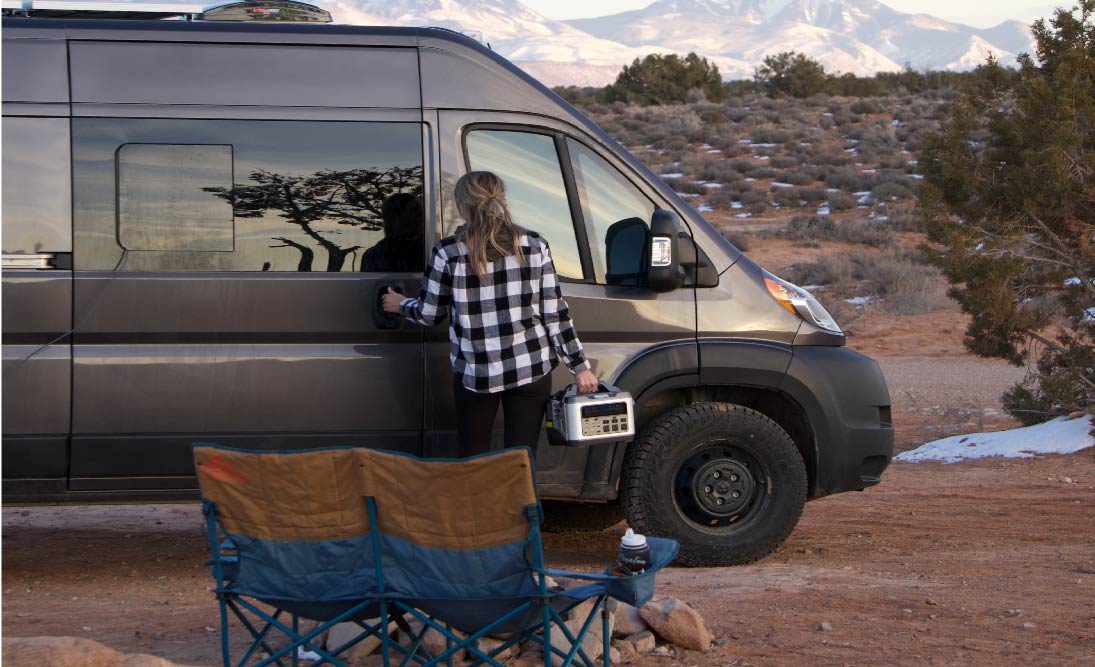
However, it's important to clarify that direct plugging of the EV or charging station into the solar panels isn't feasible. Instead, a bridge is required between the panels and the EV. This entails connecting the car to a portable power station, such as the POWEREPUBLIC T2200 or T3000, or an alternative balance of system
The portable power station acts as an intermediary that transforms and stores the energy harnessed from solar panels. This setup enables you to harness renewable energy at no cost. These portable power stations also offer multiple recharging options, including AC charging, standard car adapters, and smart generators. Notably, the POWEREPUBLIC T2200 and T3000 models possess the strength and durability to support charging via EV charging stations.
The T2200 or T3000 can be conveniently recharged in conjunction with your EV at a charging station, effectively serving as a backup power source akin to a fuel canister. This arrangement permits simultaneous charging of your vehicle and the T2200 or T3000 unit.
For those considering an investment in solar panels and portable power stations (PPS), factors like the PPS's electricity output and storage capacity should be taken into account. As an example, the POWEREPUBLIC T3000 boasts a 3000W AC power output capacity, 6000W surge, and 3200Wh of energy storage, enabling it to power nearly 95% of appliances during power outages.
Determining the EV's charging electricity requirement and your projected on-road electricity consumption is paramount. In the context of the T3000 setup described earlier, it supports a solar charging capacity of 200W. This implies the potential to connect either one 100W solar panel, one 200W solar panel, or two 100W solar panels.
Nonetheless, it's essential to consider environmental variables, particularly the extent of peak sunlight exposure your panels receive, as this significantly influences practical electricity generation. The rated power of solar panels isn't a guaranteed output; it signifies the maximum electricity production within an hour under optimal conditions.
How Many Solar Panels Do I Need For Charging An EV?

The quantity of solar panels essential for charging an electric vehicle hinges on several variables, including the rated power of the solar panels, environmental elements like peak sunlight hours, the energy consumption demands of the EV, as well as the storage capacity of both the portable power station and the electric car battery. To illustrate this, consider the following example:
For instance, the Tesla Model 3's Standard Range has a fuel economy rating of 26 kWh per 100 miles. This signifies that it utilizes 26 kWh of electricity to travel 100 miles, equating to 0.26 kWh per mile. For a daily commute of 25 miles, you would require 6.5 kWh of electricity to recharge it daily (25 miles x 0.26 kWh/mile = 6.5 kWh).
Suppose your solar array consists of 400W Rigid Solar Panels, each capable of generating 1kW of power daily, provided there are at least 2.5 hours of direct sunlight. To yield the required 6.5 kWh of energy, approximately seven 400W panels would be necessary (6.5 kWh / 1 kWh solar panel output = 6.5 solar panels). This calculation takes into account the practical output of the solar panels under prevailing sunlight conditions.
Again, the number of solar panels is determined by how many miles you want to drive for that period, the availability of the sun, and the efficiency of your solar panels.
Other Frequently Asked Questions
The Cost Of Charging an Electric Vehicle Using Solar Panels?
Apart from the initial investment outlay for a solar energy system, there are no subsequent expenses for charging an electric vehicle (EV) at home using solar power. When you connect your EV to a solar-powered outlet, the charging process is powered by electricity from the sun, incurring no costs.
Even if you complement the energy output of your solar power system with on-grid electricity, the associated expenses are considerably minor in comparison to gasoline prices. The average electricity cost in the United States is around 11.1 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Using this rate, replenishing a 40 kWh battery at home would cost approximately $4.44 (11.1 cents per kWh x 40 kWh = $4.44). In contrast, conventional gas-powered cars often demand up to $100 for a full tank in 2023.
Public charging station fees exhibit variability. Charging options could span from being free to subscription-based or pay-as-you-go based on kWh consumption, contingent on factors like location and car brand. In California, drivers typically pay between 30 and 40 cents per kWh to access a public charger. This would translate to a cost of $12-$16 for a complete charge of a 40 kWh battery (30 cents per kWh x 40 kWh = $12).
How Much Can I Save Using Solar Energy To Recharge An EV?
Typically, solar panels yield approximately $6 to $7 savings for each charging session. Once you've set up an off-grid solar panel system, the expense of charging an electric vehicle becomes zero, rendering any previous charging costs as direct savings. That’s a huge deal!
Governmental Incentives
The United States federal government extends a solar tax credit to homeowners who opt to install qualifying solar panel systems on their property. This credit can potentially offset up to 30% of the overall expenses linked to the solar panel system's cost and installation.
Beyond the federal tax credit, various states, such as California, present enticing incentives for homeowners who embrace solar panel installations. These incentives encompass possibilities like tax credits, rebates, or incentives based on performance.
Numerous states have implemented net metering regulations, allowing homeowners equipped with solar panel systems to accumulate credits for surplus energy that they generate and return to the grid. This mechanism proves instrumental in curtailing or even nullifying electricity bills, thereby augmenting the attractiveness of transitioning to solar energy.
The federal government further extends an electric vehicle (EV) tax credit aimed at new, environmentally friendly vehicles. This credit can potentially amount to $7,500 for eligible individuals and businesses.
Across various states, an array of incentives is offered to encourage the purchase of electric vehicles. These incentives range from tax credits to rebates and even special access privileges to high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lanes.
Businesses or individuals investing in EV chargers can also avail themselves of a federal tax credit. This credit corresponds to 30% of the total cost associated with the charging equipment and its installation.
These enumerated incentives represent only a fraction of the solar and EV benefits accessible to American consumers. The availability and value of these incentives tend to differ by state and may change over time. Therefore, a comprehensive exploration of the current incentives pertinent to your region is recommended.
Recharge an EV Fully Using Solar Panels, Doable Or Not?
The duration required to charge an electric vehicle (EV) with solar panels is contingent on various variables. These include the capacity of the EV's battery, its fuel efficiency, the rated power of the solar panels, their number, and the peak sunlight hours available. In broad terms, the process of fully charging an EV using solar panels might span from several hours to several days.
Conclusion
Considering solar charging for your electric vehicle (EV) can prove to be a wise investment, particularly when you take into account the available government incentives. This proposition becomes even more appealing if you reside in a state with above-average peak sunlight hours, such as Arizona, where the return on your investment can materialize more swiftly.
Even if you exclusively utilize your solar power system for EV charging, you will accumulate cost savings over time. These savings can become notably substantial if you extend the use of solar panels to power your household.
So embark on your journey today to explore solar panels, portable power stations, and power Kits, all of which enable you to harness the potent energy of the sun for both your EV and home needs!
Explore POWEREPUBLIC Portable Power Stations and Portable Solar Panels.