Table of Contents:
-
FAQ I: How To Select the Right-Sized Inverter For Your House?
-
FAQ II: How To Select the Right-Sized Battery For Your House?
-
FAQ III: How To Select the Right-Sized Solar Panel For Your House?
Individuals who have already embraced off-grid living for years possess a wealth of knowledge on constructing their solar generator system. However, for those just entering or planning to live off-grid, a common question arises: Can a solar generator effectively power a house? To address this inquiry, it's essential to understand what a solar generator is, familiarize oneself with common types, weigh the pros and cons, and learn how to choose the ideal solar generator for powering your house based on both your energy needs and budget.
We hope this article helps you find the answer to the question.
Definition of a Solar Generator

Before answering the question 'Can a solar generator power a house?' it is crucial to have a general idea of what they are and the types available.
A solar generator, also known as a solar power generator, is a device that harnesses energy from the sun and converts it into electricity. Unlike traditional generators that rely on fuel or other external sources, solar generators use photovoltaic cells to capture sunlight and generate power. These devices are commonly used in various applications, providing a clean and renewable energy source.
Components of a Solar Generator
-
Solar Panels: These are the primary components that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic process.
-
Charge Controller: This device regulates the flow of electric charge from the solar panels to the battery to prevent overcharging.
-
Battery Storage: Solar generators typically include a battery where excess energy is stored for later use when sunlight is unavailable.
-
Inverter: The inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels and stored in the battery into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in most households.
-
Outputs/Ports: Solar generators come equipped with various output ports such as USB, AC outlets, and DC outlets to allow users to power or charge different devices.
Types of Solar Generators
-
Portable Solar Generators: These are compact and lightweight units designed for easy transport. They are suitable for camping, outdoor activities, and emergency power needs. If you are searching for one, consider POWEREPUBLIC’s long-lasting and durable portable solar generator kits.
-
Stationary Solar Generators: Larger units designed for stationary use, often installed in homes, cabins, or as backup power systems.
Price Range
The price of solar generators can vary based on factors such as capacity, features, and brand. Portable solar generators could range from $200 to $1,000 or more, while stationary solar generators for home use could cost anywhere from $1,000 to several thousand dollars.
Application Scenarios
-
Emergency Power Backup: Solar generators can serve as backup power sources during power outages, ensuring a continuous power supply for critical appliances.
-
Outdoor and Camping: Portable solar generators are popular for camping trips and outdoor activities, providing a reliable and clean power source in remote locations.
-
Off-Grid Living: Solar generators are used in off-grid homes or cabins where access to traditional power sources may be limited.
-
Disaster Relief: Solar generators play a crucial role in disaster-stricken areas where access to electricity is disrupted.
-
Charging Electronic Devices: With USB ports and other charging outlets, solar generators are ideal for powering and charging small electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and cameras.
Why Do You Need a Solar Generator for Your House?

Living off-grid or simply seeking a more sustainable and resilient energy solution for your home? A solar generator could be the answer to your power needs.
Here's a detailed exploration of why you might consider integrating a solar generator into your household.
-
Clean and Renewable Energy Source: Solar generators harness energy from the sun, providing a clean and renewable power source. This eco-friendly approach reduces your carbon footprint and contributes to a more sustainable lifestyle.
-
Independence from Traditional Power Grids: Embracing a solar generator grants you independence from traditional power grids. This autonomy becomes particularly valuable during power outages or in remote locations where access to electricity may be limited.
-
Reliable Emergency Power Backup: One of the primary reasons for investing in a solar generator for your house is its reliability as an emergency power backup. When conventional power sources fail, your solar generator ensures a continuous power supply for critical appliances, ensuring comfort and safety during unforeseen outages.
-
Versatility for Various Applications: Solar generators offer versatility in applications. Whether you're camping in the great outdoors, residing in an off-grid cabin, or seeking disaster relief, these generators adapt to different scenarios. They provide a reliable power source in situations where access to electricity is disrupted or unavailable.
-
Reduced Dependency on Fossil Fuels: Unlike traditional generators that rely on fossil fuels, solar generators operate without the need for gasoline, propane, or other conventional fuels. This not only reduces operating costs but also minimizes environmental impact, contributing to a more sustainable energy landscape.
-
Cost Savings in the Long Run: While the initial investment in a solar generator may seem substantial, the long-term cost savings are noteworthy. Solar energy is essentially free once the system is in place, and with minimal maintenance requirements, the overall cost of ownership becomes economical over time.
-
Charging Electronic Devices: Solar generators are equipped with various output ports, including USB, AC, and DC outlets. This makes them ideal for powering and charging electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, cameras, and more. It provides a convenient and sustainable way to keep your essential gadgets powered, especially during emergencies.
-
Customizable Based on Power Needs and Budget: Solar generators come in various sizes and capacities, allowing you to customize your system based on your specific power needs and budget. Whether you opt for a portable unit for outdoor activities or a stationary system for home use, the flexibility in selection caters to diverse requirements.
So integrating a solar generator into your household not only aligns with environmentally conscious living but also offers practical benefits such as emergency power backup, cost savings, and versatility in application scenarios. As technology advances and solar solutions become more accessible, a solar generator stands as a reliable and sustainable investment for powering your house.
Can a Solar Generator Power a House?

Yes, it can!
However, the capability of a solar generator to effectively power a house depends on various factors, ranging from the size of your house to your specific power needs, prevailing weather conditions, and budget constraints. Let's delve into these considerations to understand whether a solar generator is a suitable solution for your household energy requirements.
1. Size of Your House
-
The square footage of your house is a critical factor in determining the energy requirements. Larger houses generally consume more electricity. For instance, a small apartment may have significantly lower energy needs compared to a spacious single-family home.
-
For instance, portable solar generator kits are often sufficient to power a small cabin or address power outages. However, for larger houses, it's advisable to invest in a comprehensive solar generator system capable of powering the entire home.
2. Power Needs
-
Evaluate the appliances and devices you intend to power. Consider essentials like refrigerators, lighting, HVAC systems, and electronic devices. Calculate their energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh) to estimate your daily and monthly power needs.
-
Example: If your refrigerator consumes 150 watts and operates for 8 hours a day, it requires 1.2 kWh per day (150 watts * 8 hours / 1000).
3. Weather Conditions
-
Assess the solar potential in your location. Consider the average daily sunlight hours, as this directly impacts the efficiency of your solar panels. Regions with more sunlight can generate more energy, making solar generators more viable.
-
Example: If your location receives an average of 5 hours of sunlight per day, a solar generator with a capacity of 5,000 watts can generate 25 kWh daily (5 hours * 5,000 watts).
4. Budget Constraints
-
Determine your budget for the solar generator system. Factor in the cost of solar panels, inverters, batteries, and installation. While a larger initial investment may provide a more powerful system, it's essential to balance this with long-term savings.
-
Example: If your budget allows, investing in a solar generator with higher capacity may offer greater energy autonomy and a faster return on investment.
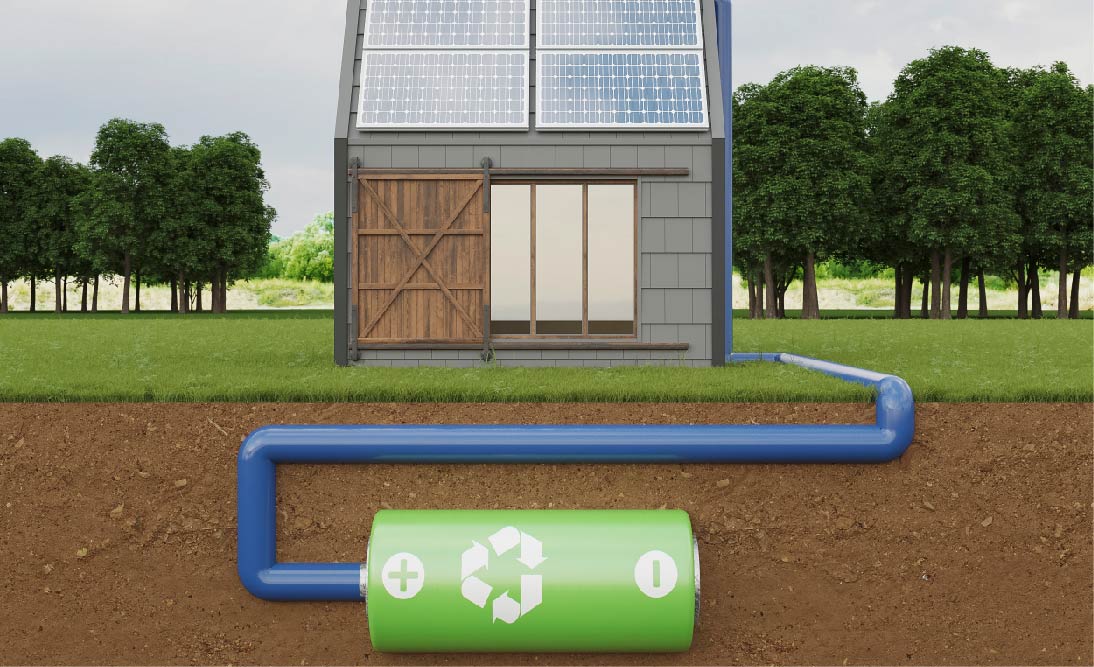
5. Energy Storage Capacity
-
Adequate battery storage is crucial for powering your house during periods without sunlight. Consider the battery capacity needed to store surplus energy generated during sunny days.
-
Example: If your daily consumption is 30 kWh, a battery storage system with a capacity of 60 kWh ensures a two-day power reserve.
6. Consulting with Solar Professionals
-
Engage with solar professionals to assess your specific needs. They can conduct a site survey, considering shading, orientation, and tilt angles to optimize your solar generator's efficiency.
-
Example: Professionals may recommend adjustments like installing solar panels at an optimal tilt angle to maximize energy capture.
7. Scalability and Future Expansion
-
Choose a solar generator system that allows for future expansion. This ensures that your system can accommodate increased energy needs as your household evolves.
-
Example: Opt for an inverter that can handle additional solar panels or batteries in the future without requiring a complete system overhaul.
8. Government Incentives and Regulations
-
Explore available incentives, rebates, and tax credits that can significantly reduce the upfront cost of installing a solar generator.
-
Example: In regions with solar incentives, a $10,000 system might effectively cost $7,000 after considering available incentives.
When addressing questions like 'Can a solar generator power a house?', a comprehensive assessment considering the size of your house, power needs, weather conditions, budget constraints, and professional advice is crucial for making an informed decision. Tailoring the system to your specific requirements ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness over time.
FAQ I: How To Select the Right-Sized Inverter For Your House?

1. Determine Your Power Needs
-
Calculate the total power consumption of all appliances you plan to run simultaneously. Add up the wattage of each device to get the peak load your inverter must handle.
-
Example: If your appliances consume a total of 2,000 watts concurrently, you'd need an inverter with a continuous output capacity of at least 2,000 watts.
2. Consider Surge Power Requirements
-
Some appliances require a higher initial surge of power when starting up. Factor in this surge power to ensure your inverter can handle the peak loads without tripping.
-
Example: A refrigerator may have a surge power requirement of 3,000 watts, so your inverter should handle both the continuous load and the occasional surge.
3. Account for Efficiency Loss
-
Inverters are not 100% efficient, and some energy is lost during the conversion process. Consider this efficiency loss when sizing your inverter. Typically, a safety margin of 10-20% is recommended.
-
Example: If your calculated load is 2,000 watts, adding a 20% safety margin brings the recommended inverter capacity to 2,400 watts.
4. Voltage Compatibility
-
Ensure the inverter's voltage compatibility matches your household needs. In most cases, residential systems use 120V or 240V AC power.
-
Example: If your house operates on a 240V system, ensure the inverter is designed to produce 240V AC output.
5. Sine Wave vs. Modified Sine Wave
-
Choose between a pure sine wave or modified sine wave inverter based on the sensitivity of your appliances. Pure sine wave inverters provide clean power and are suitable for most electronics, while modified sine wave inverters may cause issues with certain devices.
-
Example: Sensitive electronics like laptops or medical equipment benefit from a pure sine wave inverter.
FAQ II: How To Select the Right-Sized Battery For Your House?

1. Calculate Daily Energy Consumption
-
Determine your daily energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh) by adding up the energy requirements of all appliances over a day.
-
Example: If your daily consumption is 30 kWh, the battery capacity should be able to provide at least this amount of energy.
2. Consider Days of Autonomy
-
Decide how many days you want the battery to support your house without solar input. Multiply your daily consumption by the desired autonomy days.
-
Example: If you want three days of autonomy and your daily consumption is 30 kWh, the required battery capacity is 90 kWh (30 kWh/day * 3 days).
3. Depth of Discharge (DoD)
-
Batteries are typically rated for a certain depth of discharge, indicating the percentage of the battery's capacity that can be safely used. Choose a DoD that balances cost and battery lifespan.
-
Example: If you have a 100 kWh battery with an 80% DoD, you can effectively use 80 kWh of the total capacity.
4. Voltage Compatibility
-
Ensure the battery's voltage matches your inverter's requirements. Common residential systems use 12V, 24V, or 48V batteries.
-
Example: If your inverter operates at 48V, choose a battery bank that also operates at 48V.
5. Consider Battery Chemistry
-
Different battery chemistries (lead-acid, lithium-ion, etc.) have different characteristics in terms of lifespan, depth of discharge, and maintenance. Choose a chemistry that aligns with your preferences and budget.
-
Example: Lithium-ion batteries often have a longer lifespan and higher depth of discharge compared to lead-acid batteries.
FAQ III: How To Select the Right-Sized Solar Panel For Your House?

1. Calculate Daily Energy Production
-
Estimate the daily energy production required to meet your energy needs. This is influenced by your daily consumption and the sunlight hours in your location.
-
Example: If your daily consumption is 30 kWh and you receive an average of 5 hours of sunlight, you need a solar array capable of producing at least 6 kW (30 kWh / 5 hours).
2. Consider Panel Efficiency
-
Solar panels have different efficiency ratings. Higher efficiency panels produce more power in limited space but may be costlier. Choose panels based on your available space and budget.
-
Example: If you have limited roof space, higher efficiency panels may be a better choice to maximize energy production.
3. Account for Tilt and Orientation
-
Optimize your solar panel setup by considering the tilt angle and orientation. Panels facing south at an optimal tilt angle capture more sunlight.
-
Example: Adjusting panels to face south at a tilt angle equal to your latitude can significantly improve energy production.
4. Size of Your Roof or Available Space
-
Consider the available space for solar panel installation. Larger roofs or open areas allow for more extensive solar arrays.
-
Example: If your roof has an area of 50 square meters and your chosen solar panels have an efficiency of 20%, you could install a system capable of producing 10 kW (50 sq.m * 20%).
5. Balance Energy Production and Consumption
-
Align your solar panel capacity with your energy consumption to achieve a balance between energy production and usage.
-
Example: If your daily consumption is 30 kWh and your solar array produces 40 kWh, you have room for expansion or surplus energy.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the question 'Can a solar generator power a house?' depends on various factors such as house size, energy needs, weather conditions, and budget constraints. While portable solar generator kits may suffice for smaller spaces or specific applications, larger houses may benefit from a comprehensive solar generator system. Considerations include assessing daily energy consumption, accounting for surge power requirements, factoring in weather conditions, and aligning the system with budgetary considerations. Professional consultation, scalability for future expansion, and exploring government incentives further enhance the decision-making process.
Ultimately, a well-calibrated solar generator not only aligns with environmentally conscious living but also offers practical benefits such as emergency power backup, cost savings, and versatile application scenarios. So, can a solar generator power a house? Yes, with careful planning and customization, a solar generator can effectively power a house, providing a sustainable and reliable energy solution.