Table of Contents:
-
FAQ I: Choose an Inverter For Solar Power Supply - What Should I Consider?
-
FAQ II: Choose a Battery For Solar Power Supply - What Should I Consider?
-
FAQ III: Choose Solar Panels For Solar Power Supply - What Should I Consider?
Solar power has become one of the most popular power solutions among people who live off-grid or in areas with extreme weather. Additionally, for those who frequently engage in camping, overlanding, and car camping, having a reliable solar power supply ensures that their devices and appliances stay charged, enhancing their overall experience.
If you are wondering, curious, or in search of a reliable solar power supply, you are in the right place. In this blog, we will provide a brief guide on what solar power supply is, discuss various options, highlight the pros and cons, and offer insights on choosing the ideal solar power supply for your needs. We will also introduce POWEREPUBLIC solar generator kits as an excellent option.
What is Solar Power Supply?

Solar power supply refers to the utilization of solar energy, derived from the sun, to generate electricity and power various devices and systems. This process involves harnessing sunlight and converting it into electrical energy through the use of solar panels, which are composed of photovoltaic cells. These cells contain semiconductor materials that absorb photons from sunlight and generate an electric current.
Here is a detailed breakdown of the components and workings of solar power supply:
Solar Panels
-
Solar panels, also known as solar modules, are the primary components responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. They consist of numerous photovoltaic cells linked together. These cells generate direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
-
The two main types of solar panels are poly-crystalline and mono-crystalline solar panels. Each has its benefits and drawbacks.
Inverter
-
The direct current produced by solar panels is converted into alternating current (AC) by an inverter. AC is the standard form of electricity used in homes and most electrical devices.
Mounting Structure
-
Solar panels are typically mounted on structures that allow them to capture sunlight at an optimal angle. This mounting structure can be fixed or adjustable based on the system's design and requirements.
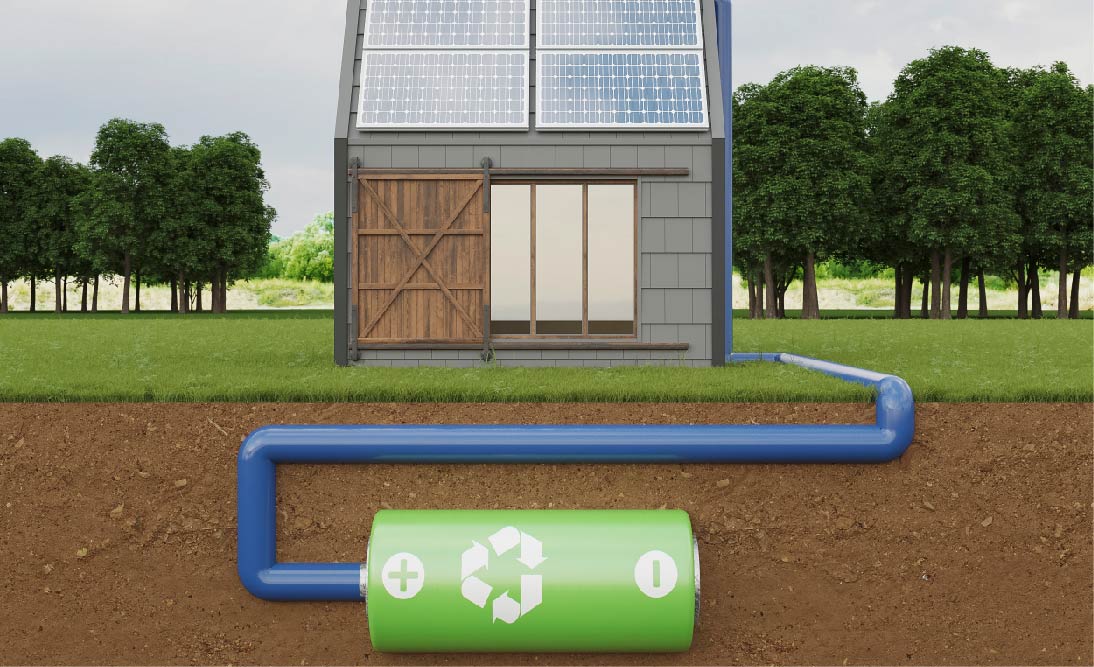
Battery Storage (Optional)
-
In some solar power systems, a battery storage component is included. This allows excess electricity generated during sunny periods to be stored for later use, such as during nighttime or on cloudy days. It enhances the reliability and availability of solar power.
Charge Controller (Optional)
-
For systems with battery storage, a charge controller is often used to regulate the charging and discharging of the batteries. This helps prevent overcharging and extends the lifespan of the batteries.
Grid Connection (Optional)
-
Solar power systems can be connected to the electrical grid, allowing users to either draw electricity from the grid when solar production is low or sell excess electricity back to the grid, depending on local regulations and policies.
Monitoring System
-
Many solar power systems come equipped with monitoring tools that allow users to track the performance of their solar panels and overall system efficiency.
The advantages of solar power supply include its renewable nature, reduced environmental impact, and potential cost savings over time. However, challenges such as intermittency (dependence on sunlight), initial installation costs, and space requirements should be considered when implementing solar power systems. Advances in technology and decreasing costs continue to make solar power an increasingly viable and attractive energy solution. We will talk about these advantages and disadvantages later.
Options for Solar Power Supply and Price Range

There are different options for solar power supply. We have listed a few that are used frequently these days. Knowing them will help you make a better decision about how to select the best solar power supply according to your needs.
Portable Solar Chargers
-
Description: Compact solar chargers are designed for small electronics like smartphones and USB-powered devices. Ideal for hiking, camping, and day trips.
-
Price Range: $20 to $150 or more.
Solar Power Banks
-
Description: Power banks with integrated solar panels for charging on the go. Suitable for charging multiple devices and often includes features like LED flashlights.
-
Price Range: $30 to $200 or more.
Portable Solar Generator Kits (Power Station + Solar Panel)
-
Description: Compact and portable solar power solutions that include a power station and a portable solar panel. These kits are versatile and suitable for camping, overlanding, and emergency power needs.
-
Price Range: $200 to $3,000 or more.
Grid-Tied Solar Systems
-
Description: Larger solar installations connected to the electrical grid. Suitable for residential and commercial use, providing continuous power supply and potential energy bill savings.
-
Price Range: $10,000 to $30,000 or more.
Off-Grid Solar Systems
-
Description: Independent solar power solutions with solar panels, inverters, battery storage, and sometimes backup generators. They are designed for remote locations without access to the grid.
-
Price Range: $5,000 to $50,000 or more.
Remember that the price ranges of these solar power supply options are approximate and may vary based on factors like brand, quality, and additional features. Installation costs should also be considered for larger systems, especially those requiring professional setup.
Pros and Cons of Solar Power Supply

After familiarizing yourself with the various options for solar power supply, it's essential to explore their respective pros and cons. This exploration will provide a deeper understanding of each option, enabling you to make a well-informed decision.
Portable Solar Chargers
Pros:
-
Portability: Compact and lightweight, making them highly portable for outdoor activities.
-
Convenience: Ideal for charging small electronics like smartphones and USB-powered devices.
-
Affordability: Generally more cost-effective compared to larger solar power solutions.
-
Ease of Use: Simple setup and user-friendly for on-the-go charging.
-
Versatility: Can be used for various outdoor activities such as hiking and camping.
Cons:
-
Limited Capacity: Suited for small devices; may not provide sufficient power for larger electronics.
-
Weather Dependency: Performance may be affected during cloudy or low sunlight conditions.
-
Slow Charging: May take longer to charge devices compared to other solar options.
Solar Power Banks
Pros:
-
Portability and Versatility: Compact and portable with the added convenience of built-in solar panels.
-
Convenience: Suitable for charging various devices on the go.
-
Compact Design: Fits well in backpacks or pockets.
-
Emergency Power: This can serve as backup power during power outages.
Cons:
-
Limited Capacity: This may not provide sufficient power for larger devices or multiple charges.
-
Weather Dependency: Solar charging may be slow, and efficiency depends on sunlight conditions.
-
Battery Degradation: The built-in battery may degrade over time.
Portable Solar Generator Kits (Power Station + Solar Panel)
Pros:
-
Versatility: Provides a compact and versatile solution for various power needs.
-
Suitable for Camping: Ideal for camping, overlanding, and emergencies.
-
Multiple Charging Ports: You can charge multiple devices simultaneously.
-
Expandable: Some kits allow for the addition of extra solar panels for increased power generation.
-
Off-Grid Capability: Offers independence from the electrical grid.
Cons:
-
Cost: The initial cost may be higher compared to individual chargers or power banks.
-
Weight: While portable, may be heavier than smaller solar chargers.
-
Limited Power Output: This may not be suitable for high-power demand or prolonged use.
Grid-Tied Solar Systems
Pros:
-
Continuous Power Supply: Provides a continuous and reliable power supply connected to the grid.
-
Energy Bill Savings: This can lead to reduced energy bills through net metering and selling excess power.
-
Low Maintenance: Generally low maintenance once installed.
-
Government Incentives: Eligible for government incentives and rebates.
Cons:
-
High Initial Cost: Installation costs can be significant.
-
Dependency on Grid: Rely on the grid during periods of low solar generation.
-
Complex Installation: Requires professional installation and may involve complex permitting processes.
Off-Grid Solar Systems
Pros:
-
Energy Independence: Provides independence from the electrical grid.
-
Suitable for Remote Areas: Ideal for remote locations without grid access.
-
Environmental Impact: Reduced carbon footprint and environmental impact.
-
Long-Term Cost Savings: Potential long-term savings on energy bills.
Cons:
-
High Initial Cost: Installation costs can be substantial.
-
Maintenance: Requires periodic maintenance of components like batteries and inverters.
-
Space Requirements: Larger systems may need significant space.
Note: Prices mentioned earlier are approximate and may vary based on brand, quality, and additional features. Installation costs should also be considered, especially for larger systems requiring professional setup.
How To Choose The Ideal Solar Power Supply?

Selecting the best solar power supply involves careful consideration of your energy needs, location, budget, and preferences.
Here's a detailed guide to help you make an informed decision:
Assess Your Energy Needs
-
List all the devices you intend to power using solar energy.
-
Note the power consumption in watts (W) or kilowatt-hours (kWh) per day for each device.
-
For example: If you have a refrigerator consuming 150W and you run it for 24 hours, it requires 3.6 kWh per day (150W × 24 hours/1000).
-
Also, pay attention to the surge power(peak power) of your devices. Some appliances like refrigerators need a certain amount of power when starting, usually double or triple their rated power. Make sure you consider that as well.
Calculate Your Total Daily Energy Consumption
-
Sum up the daily energy consumption of all devices to determine your total daily energy needs.
-
For example: Refrigerator (3.6 kWh) + Lights (1 kWh) + Laptop (0.5 kWh) = 5.1 kWh per day.
Consider Your Location
-
Determine the average sunlight hours in your location using solar irradiance maps.
-
Assess shading, weather patterns, and seasonal variations.
-
For example: If you live in an area with an average of 4 hours of sunlight per day, you'd need a system capable of generating at least 5.1 kWh / 4 hours = 1.275 kW.
Set Your Budget
-
Define a budget that covers the solar power system, installation, and additional components.
-
Consider long-term savings and return on investment (ROI).
-
For example: Suppose your budget is $3,000, and your estimated annual savings are $800. Your ROI would be ($800 - $3,000) / $3,000 × 100 = -60%, indicating a negative ROI.
Choose the System Type
-
On-Grid System: Connected to the electrical grid, suitable for areas with reliable grid access.
-
Off-Grid System: Independent of the grid, ideal for remote locations without grid access.
-
Hybrid System: Combines grid-tied and off-grid capabilities.
-
For example: If you live in an urban area with reliable grid access, an on-grid system may be more cost-effective.
Select Solar Panel Type
-
Monocrystalline panels are more efficient but costlier than polycrystalline panels.
-
Consider space availability, efficiency, and budget.
-
For example: If space is limited, and budget allows, opt for monocrystalline panels.
-
If you want to know more about how to choose solar panels, click here for more info.
Battery Storage Consideration
-
Calculate the required battery capacity for storing excess energy.
-
Consider the depth of discharge (DoD) and the number of cycles the batteries can endure.
-
For example: If your daily consumption is 5.1 kWh, a 10 kWh battery with 50% DoD is suitable.
-
If you want to know more about how to choose a battery, click here for more info.
Choose an Inverter
-
Select an inverter that matches the system's voltage and type.
-
Consider features like grid synchronization for grid-tied systems.
-
For example: If you have a 48V battery bank, choose a 48V inverter.
-
If you want to know more about how to choose an inverter, click here for more info.
Factor in System Efficiency
-
Assess the efficiency of solar panels, inverters, and batteries.
-
Aim for a system with high overall efficiency to maximize energy production.
-
For example: An 85% efficient inverter converts 85% of the energy from solar panels to usable electricity.
Explore Government Incentives
-
Research local and federal incentives, tax credits, and rebates to offset costs.
-
For example: A $500 rebate can significantly impact your overall budget.
Warranty and System Lifespan
-
Review warranties provided by manufacturers for solar panels, inverters, and batteries.
-
Consider the expected lifespan of each component.
-
For example: A 10-year or more warranty on solar panels indicates durability.
Professional Installation
-
While DIY is an option, professional installation ensures compliance with regulations.
-
Obtain quotes from reputable solar installation companies.
-
For example: Professional installation might cost $2,000 but ensures safety and adherence to local codes.
By systematically considering these factors, performing calculations, and using examples, you can confidently select the best solar power supply that aligns with your specific needs and circumstances.
POWEREPUBLIC Solar Generator Kits as Solar Power Supply
As mentioned earlier, portable solar generator kits provide one option for solar power supply, comprising a portable power station and a portable solar panel. Paired together, these kits offer versatility and are suitable for camping, overlanding, and emergency power needs.
POWEREPUBLIC offers four different solar generator kits, each designed for reliable and long-lasting solar power supply. Each kit is tailored for specific scenarios and power requirements, allowing you to choose the one that perfectly matches your needs.
Please note that:
To estimate the working time, we use the formula below:
Working Time(Hours)= Capacity of the Portable Power Station(Wh)*0.85(conversion rate)/ Rated Power of the Devices(W)
Option I: POWEREPUBLIC T306 + 100W Portable Solar Panel

For those outdoor lovers who are looking for a solar power supply to keep their essential devices charged, our T306+PV100 solar generator kits would be an excellent choice. Our T306 models(300W/296Wh, surge 600W) and 100W portable solar panels are less than 10 pounds, making them super handy, easy to carry around with you, and won’t take up too much of your space. Portability is the key advantage of our T306+PV100 combo.
Also, the amazing 10 output ports allow you to charge up to 10 devices at the same time so that you don’t have to worry about not having enough outlets for your essential gear.
Here is a table showing some frequently used devices during camping and the working time of POWEREPUBLIC T306 + PV100 solar generator kits:
|
Devices |
Rated Power (W) |
Estimated Working Time (hours) |
|
LED Lantern |
5 |
50 |
|
Portable Heater |
150 |
1.5 |
|
Camping Stove |
100 |
2.5 |
|
Portable Fan |
10 |
25 |
|
GPS Device |
2 |
125.5 |
|
Portable Coffee Maker |
60 |
4 |
|
Rechargeable Flashlight |
3 |
88.6 |
|
Portable Speaker |
8 |
31.5 |
|
Handheld Radio |
1 |
314 |
Option II: POWEREPUBLIC T1200 + 100W Portable Solar Panel or T1200 + 200W Portable Solar Panel

For those seeking a solar power supply to keep some larger appliances such as blenders, coffee machines, TVs, and electric blankets charged, our T1200+PV100 or T1200+PV200 solar generator kits would be excellent choices. The T1200 models(1200W/1110Wh, surge 2600W) are designed to strike a balance between portability and functionality, allowing you to pair them with either a 100W or 200W portable solar panel. Opt for the T1200+PV200 combo for higher solar input or the T1200+PV100 combo if you don't need as much.
Additionally, the impressive 13 output ports enable you to charge up to 13 devices simultaneously, ensuring you can power both essential devices and larger items simultaneously.
Here is a table showing some frequently used devices and items during camping, along with the working time of POWEREPUBLIC T1200 + PV100 and T1200+PV200 solar generator kits:
|
Devices |
Rated Power (W) |
Estimated Working Time (hours) |
|
Portable TV |
50 |
18.5 |
|
Coffee Machine |
800 |
1 |
|
Electric Grill |
1000 |
1 |
|
Electric Blanket |
75 |
11.5 |
|
Portable Air Conditioner |
1200 |
0.5 |
|
Blender |
200 |
4.5 |
|
Laptop |
60 |
14 |
|
Portable Heater |
1500 |
0.5 |
|
Electric Kettle |
100 |
10.5 |
|
Camping Fridge |
80 |
13 |
Option III: POWEREPUBLIC T2200 + 200W Portable Solar Panel

For those seeking a solar power supply to keep home appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves, and water heaters charged, our T2200+PV200 solar generator kit is an excellent choice. The T2200 models (2200W/2240Wh, surge 4500W) are designed with a larger battery capacity to support home appliances during power outages. If you live off-grid or are looking for a reliable power solution to energize your small cabin, consider the POWEREPUBLIC T2200+PV200 combo.
Additionally, the impressive 15 output ports enable you to charge up to 15 devices and appliances simultaneously, ensuring you can power almost 90% of your devices and appliances. The functionality of the T2200 makes it an ideal indoor generator.
Here is a table showing some frequently used devices and items during camping, along with the working time of the POWEREPUBLIC T2200+PV200 solar generator kits:
|
Devices |
Rated Power (W) |
Estimated Working Time (2240Wh) |
|
Washing Machine |
1200 |
1.5 |
|
Microwave |
800 |
2 |
|
Hair Dryer |
1500 |
1 |
|
Water Pump |
500 |
4.5 |
|
Blender |
300 |
7 |
|
Portable Air Conditioner |
1200 |
1.5 |
|
Vacuum Cleaner |
1000 |
1 |
|
Toaster |
700 |
2 |
|
Electric Grill |
1500 |
1 |
|
Water Heater |
2000 |
1 |
Option IV: POWEREPUBLIC T3000 + 200W Portable Solar Panel

For those seeking a solar power supply to keep home appliances charged and serve as a whole-house solar generator, our T3000+PV200 solar generator kit is an excellent choice. The T3000 model (3000W/3200Wh, surge 6000W) is designed as a home backup power solution during power outages. If you live off-grid or are looking for a reliable power solution to energize your home or vehicles, consider the POWEREPUBLIC T3000+PV200 combo. Also, since the battery capacity of our T3000 model is large, you can use it as a home battery backup without solar. The versatility of the T3000 makes it an ideal indoor generator.
Additionally, the impressive 15 output ports enable you to charge up to 15 devices and appliances simultaneously, ensuring you can power almost 95% of your devices and appliances.
Here is a table showing some frequently used devices and items during camping, along with the working time of the POWEREPUBLIC T3000+PV200 solar generator kit:
|
Devices |
Rated Power (W) |
Estimated Working Time (3200Wh) |
|
Washing Machine |
1200 |
2 |
|
Microwave |
800 |
2.5 |
|
Hair Dryer |
1500 |
0.5 - 1 |
|
Water Pump |
500 |
6.5 |
|
Blender |
300 |
9.5 |
|
Portable Air Conditioner |
1200 |
2 |
|
Vacuum Cleaner |
1000 |
0.5 - 0.7 |
|
Toaster |
700 |
3 |
|
Electric Grill |
1500 |
0.5 |
|
Water Heater |
2000 |
0.5 |
FAQ I: Choose an Inverter For Solar Power Supply - What Should I Consider?

Inverter Type
-
Consideration: Pure Sine Wave vs. Modified Sine Wave
-
Example: A medical device may require a pure sine wave inverter for stable operation. Choosing a modified sine wave inverter might lead to performance issues.
Power Rating
-
Consideration: Continuous Power vs. Surge Power
-
Calculation: If your devices require a total of 1500W, and the surge power during startup is 3000W, choose an inverter with a continuous power rating above 1500W and surge power above 3000W to handle peak loads.
Waveform Compatibility
-
Consideration: Compatibility with Device Waveform
-
Example: Sensitive electronics like laptops and audio equipment may require a pure sine wave inverter to prevent interference and damage.
Efficiency
-
Consideration: Efficiency Rating
-
Estimation: Choose an inverter with an efficiency rating of 90% or higher to minimize energy loss during conversion.
Input Voltage Range
-
Consideration: Compatibility with Solar System Voltage
-
Example: If your solar panel system operates at 24V, select an inverter that accepts input within that voltage range.
Click here if you want to know more about how to select an inverter.
FAQ II: Choose a Battery For Solar Power Supply - What Should I Consider?

Battery Type
-
Consideration: Lead-acid vs. Lithium-ion
-
Example: For a small off-grid cabin, where weight is not a concern, a lead-acid battery may be a cost-effective choice. However, for a portable solar generator, a lithium-ion battery's lighter weight could be advantageous.
Capacity (Ah)
-
Consideration: Daily Energy Consumption
-
Calculation: If your daily energy consumption is 500Wh, and your system operates at 12V, you'd need a battery with at least 41.7Ah (500Wh / 12V).
Depth of Discharge (DoD)
-
Consideration: Depth to Which the Battery is Discharged
-
Example: A 50% DoD means you can use half of the battery's capacity before recharging, extending the battery's lifespan.
Cycle Life
-
Consideration: Number of Charge-Discharge Cycles
-
Estimation: Lithium-ion batteries often have a cycle life of 2000 cycles or more, while lead-acid batteries typically offer around 500 cycles.
Charging Speed
-
Consideration: Charging Time
-
Example: A 100Ah lithium-ion battery might charge in 5 hours with a 20A charger.
Click here if you want to know more about how to select the battery.
FAQ III: Choose Solar Panels For Solar Power Supply - What Should I Consider?

Solar Panel Type
-
Consideration: Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline vs. Thin-Film
-
Example: Monocrystalline panels are space-efficient and suitable for limited roof space.
Efficiency
-
Consideration: Efficiency Rating
-
Estimation: Monocrystalline panels often have efficiency ratings above 20%, while polycrystalline panels may range from 15-18%.
Space Availability
-
Consideration: Available Installation Space
-
Example: For small spaces, consider high-efficiency monocrystalline panels.
Durability
-
Consideration: Quality and Construction
-
Estimation: Quality panels come with durable frames and tempered glass for protection.
Temperature Coefficient
-
Consideration: Efficiency in Different Temperatures
-
Example: A lower temperature coefficient, e.g., -0.3%/°C, means the panel's efficiency decreases less with rising temperatures.
Wattage and Size Estimation
-
Consideration: Estimating Panel Size
-
Calculation: If your daily energy needs are 500Wh, and you receive an average of 5 hours of sunlight per day, you'd need a panel with a capacity of 100W (500Wh / 5 hours).
Click here if you want to know more about how to find out the total power of the solar panels you need.
Click here if you want to know more about how to find out the number of solar panels you need.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, solar power supply offers a sustainable and versatile solution for various energy needs. From portable solar chargers to whole-house solar generators, the options cater to different lifestyles and preferences. Assessing your energy requirements, considering location factors, and setting a budget are crucial steps in choosing the ideal solar power supply.
POWEREPUBLIC's solar generator kits provide reliable options, each tailored to specific scenarios, ensuring a seamless integration of solar energy into daily life. Whether for camping, emergencies, or powering home appliances, solar power supply offers a cleaner and cost-effective energy alternative. Explore the diverse options available and embrace the benefits of harnessing sunlight to power your devices and appliances. Make the switch to solar power for a greener and more sustainable energy future.